K8S again
A k8s intro in Chinese from this video. It explains k8s concepts in a much clear way and I finally feel that I understand the architecture of k8s
1 Services
Let’s review ks8 components again
-
Pod
Pod can have one or more containers. The best practice is one, and others are called side cars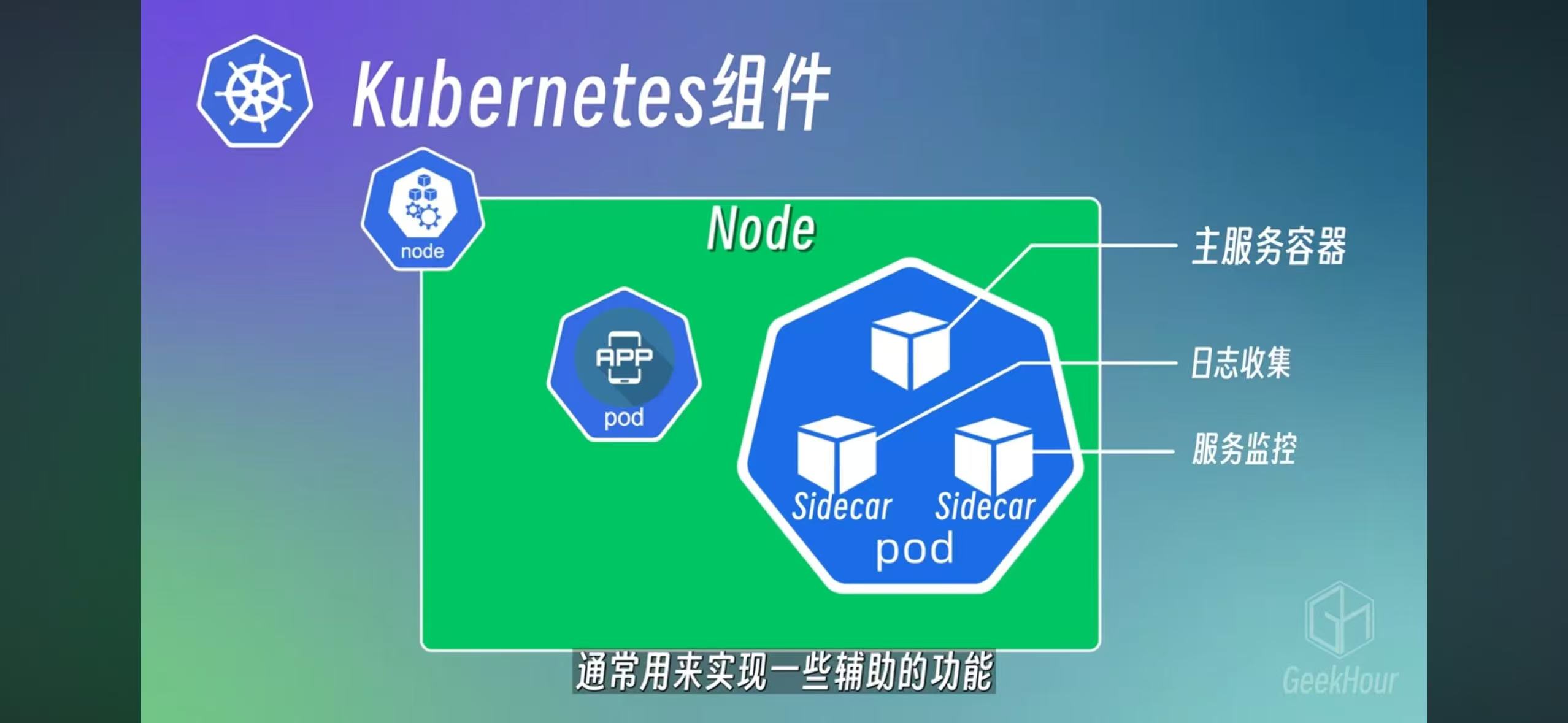
-
Service and NodePort
Pod’s interal IP may change, so create a service can have fixed access to pod. and nodeport can be used for external access with a external facing port number.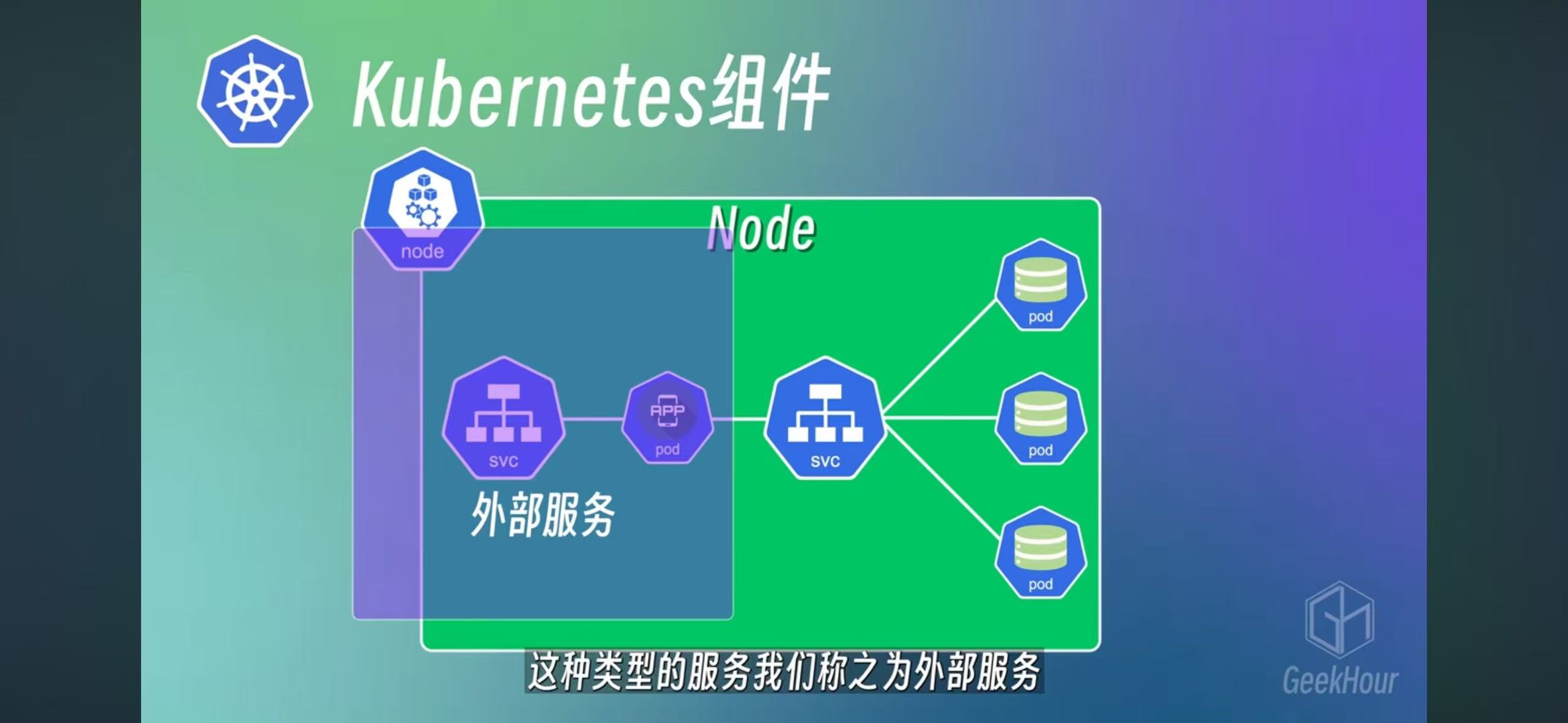
-
Ingress
Ing is for external URL access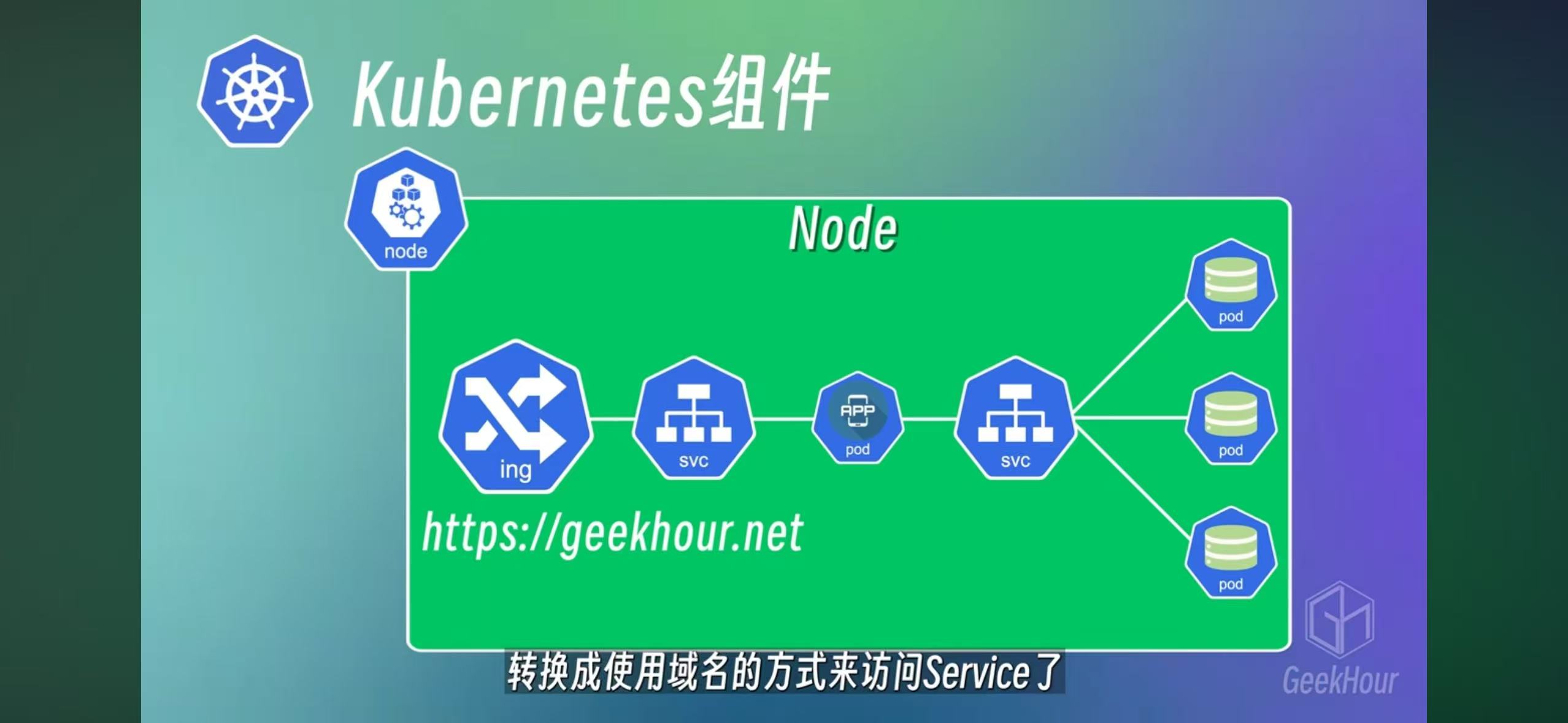
-
ConfigMap and Secrets
Both are used to record config data. Secrets used base64 encoding, so it’s not really secret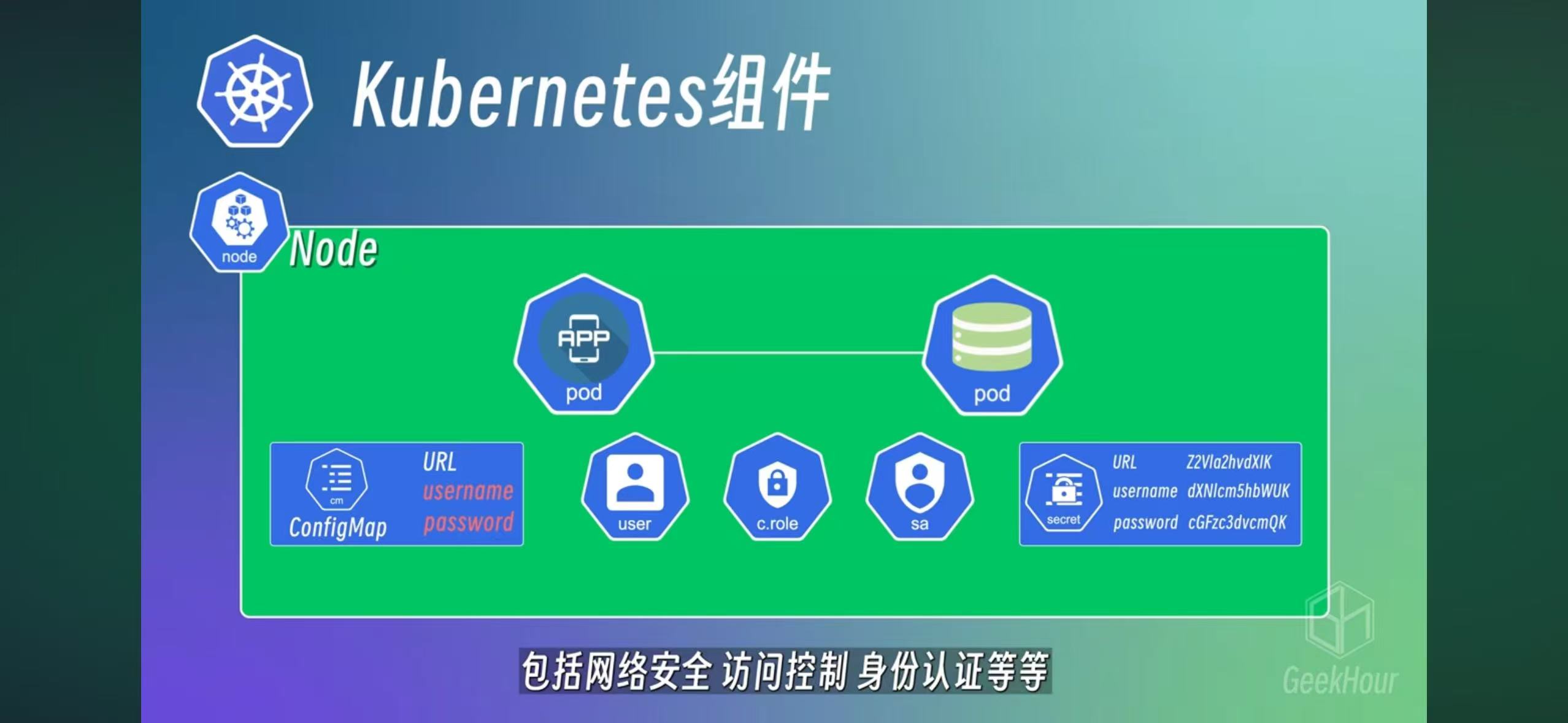
-
Deployment
A group of pods can be deployed by a deployment. and ReplicaSet is between pod and deployment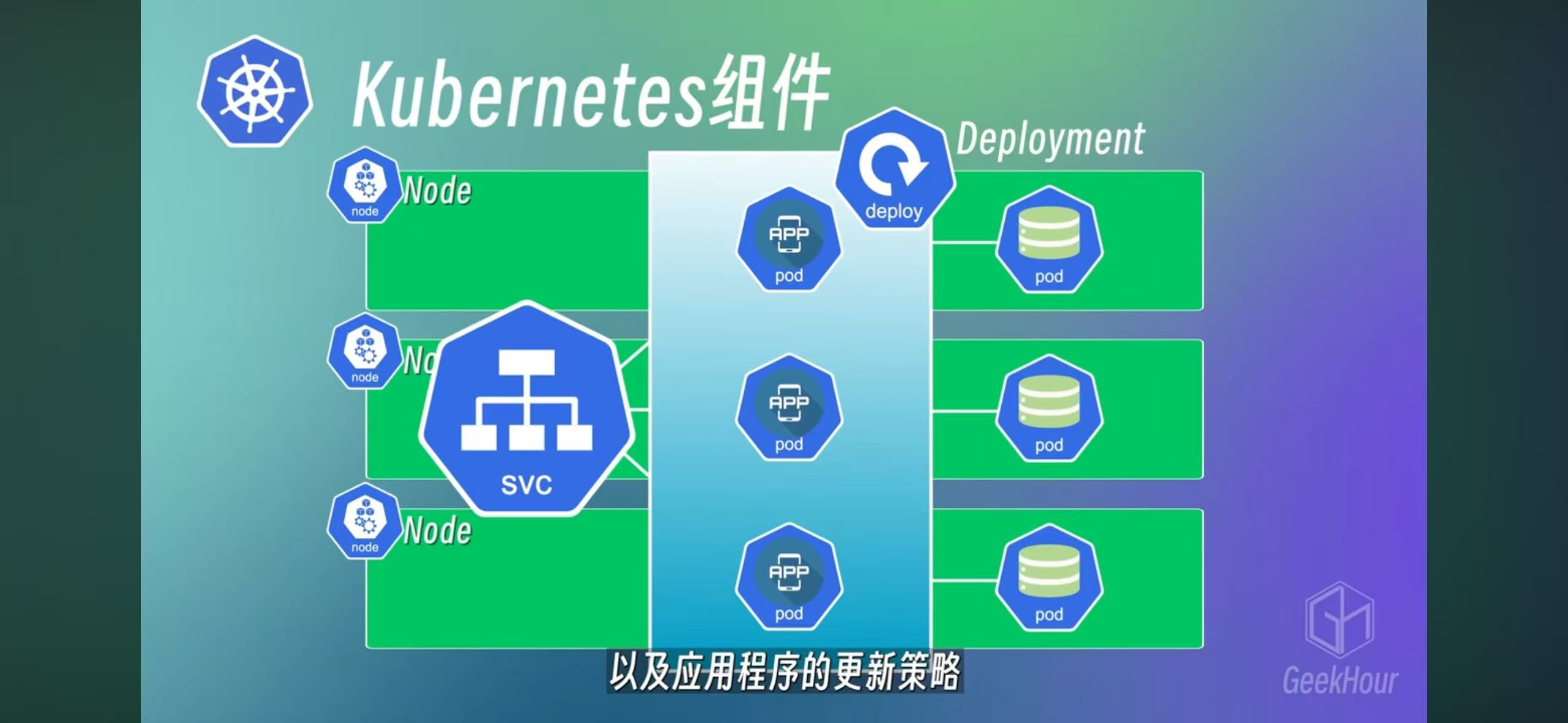 Statefulset is a deployment for database
Statefulset is a deployment for database
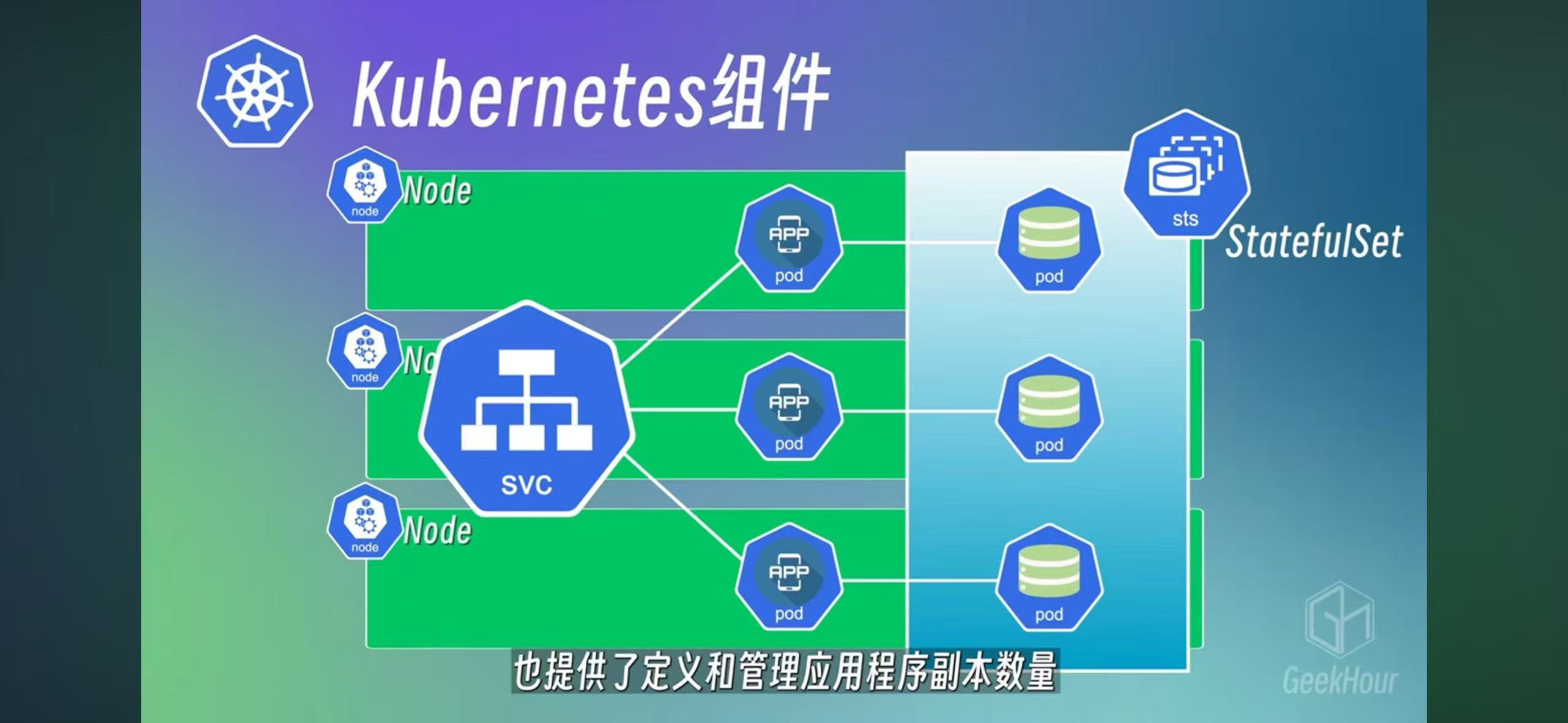
2 Master and Worker nodes
A worker has kubelet, kube-proxy(for networking), and a container runtime
 Master is build around APIServer to interact with kubectrl command
Master is build around APIServer to interact with kubectrl command
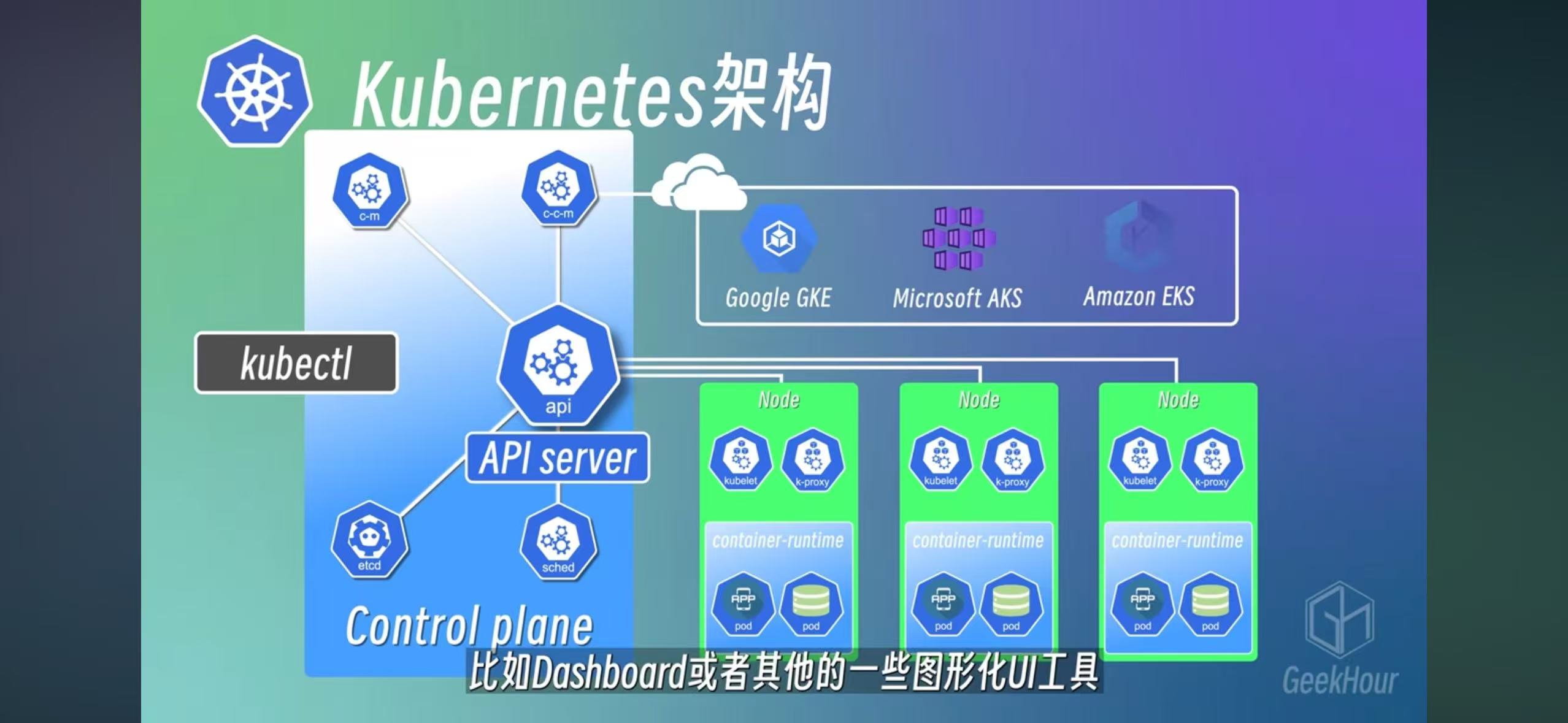
- API Server: Gateway to the k8s
- Scheduler: monitor resource usage for all services, assign pod into node
- c-m: Control Mangaer, check resource status
- etcd: Key-value storeage, similar to redis. It’s the brain of k8s and record all data for k8s
- c-c-m: Cloud-control-Manager, for connecting with EKS/AKS/GKS
3 K8S setup
- minukube: Creating a single node K8s
- multipass + k3s: A mini VM ware + mutile node k8s
- killacoda: online k8s sandbox
4 Examples
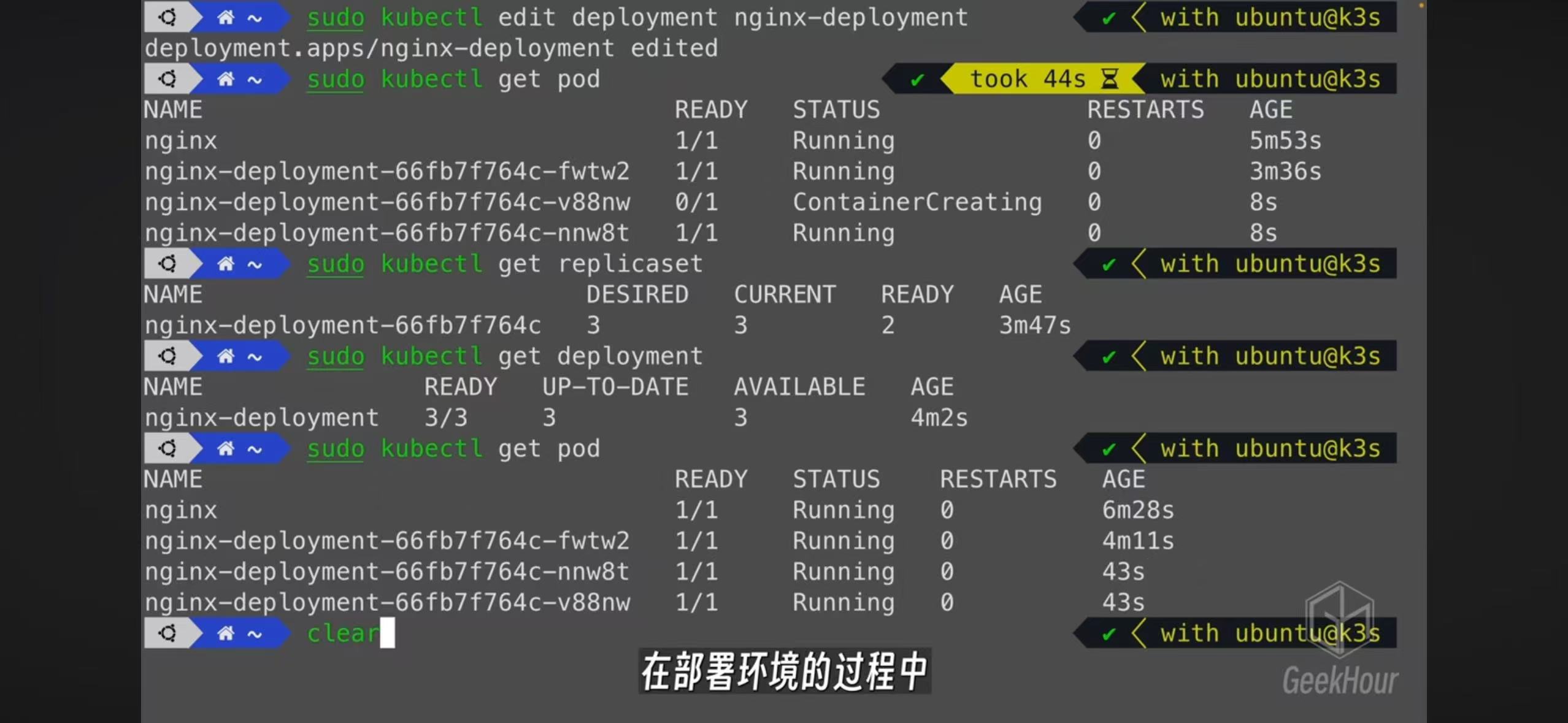
- The best practice of creating a pod is by creating a deployment. A replicaset will be create and also a pod
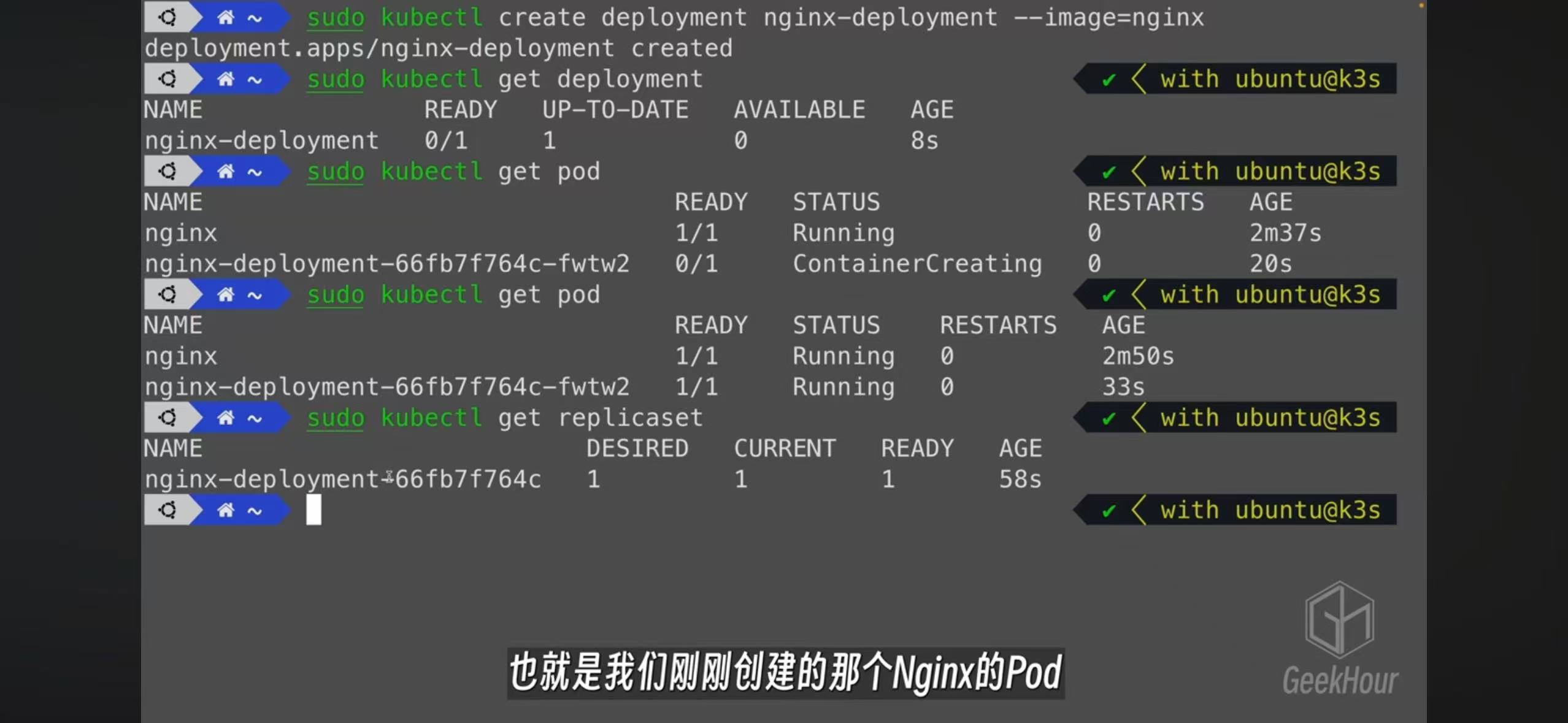
- Edit a deployment will automatically create cooresponding replicatset and pods
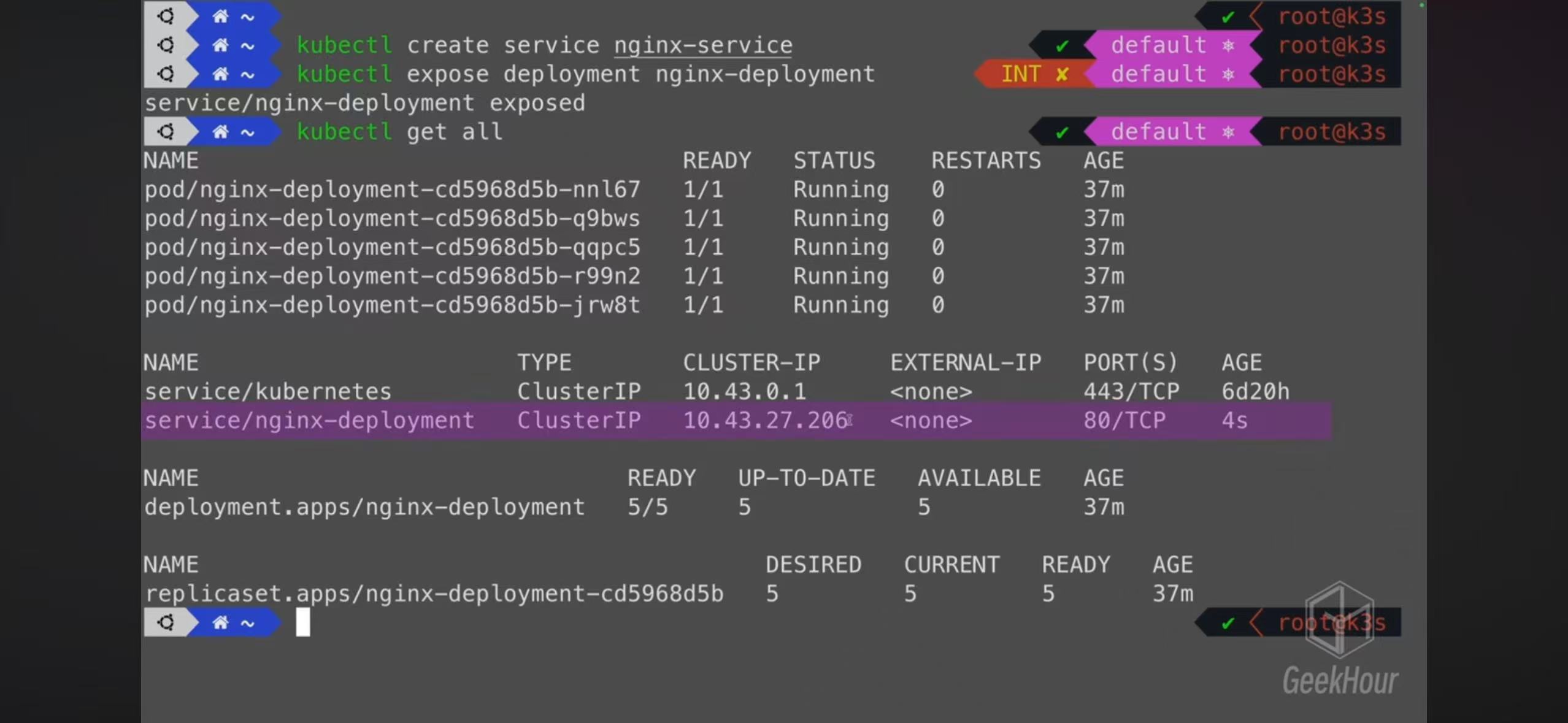
- You can create a service or expose a deployment
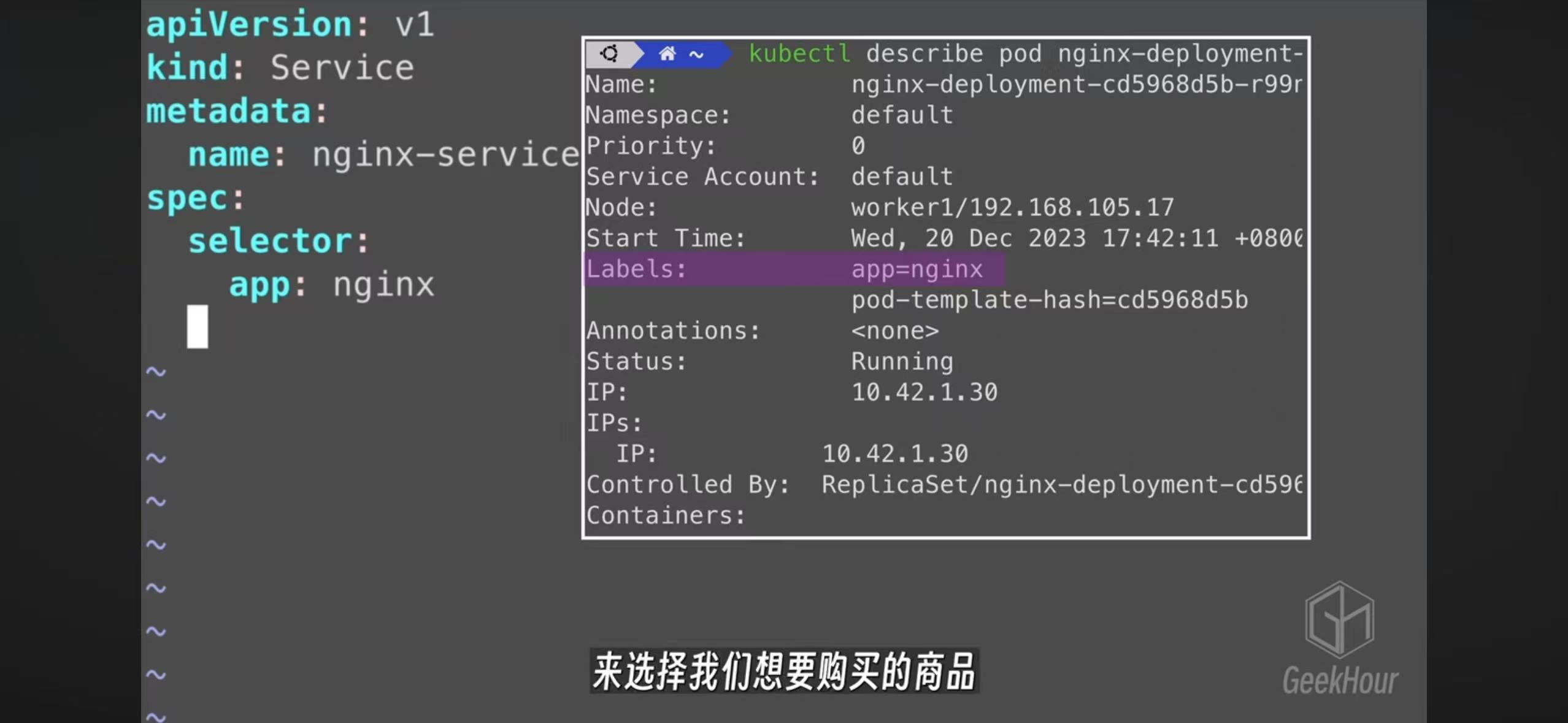
- The service config file use selector to match with pod labels
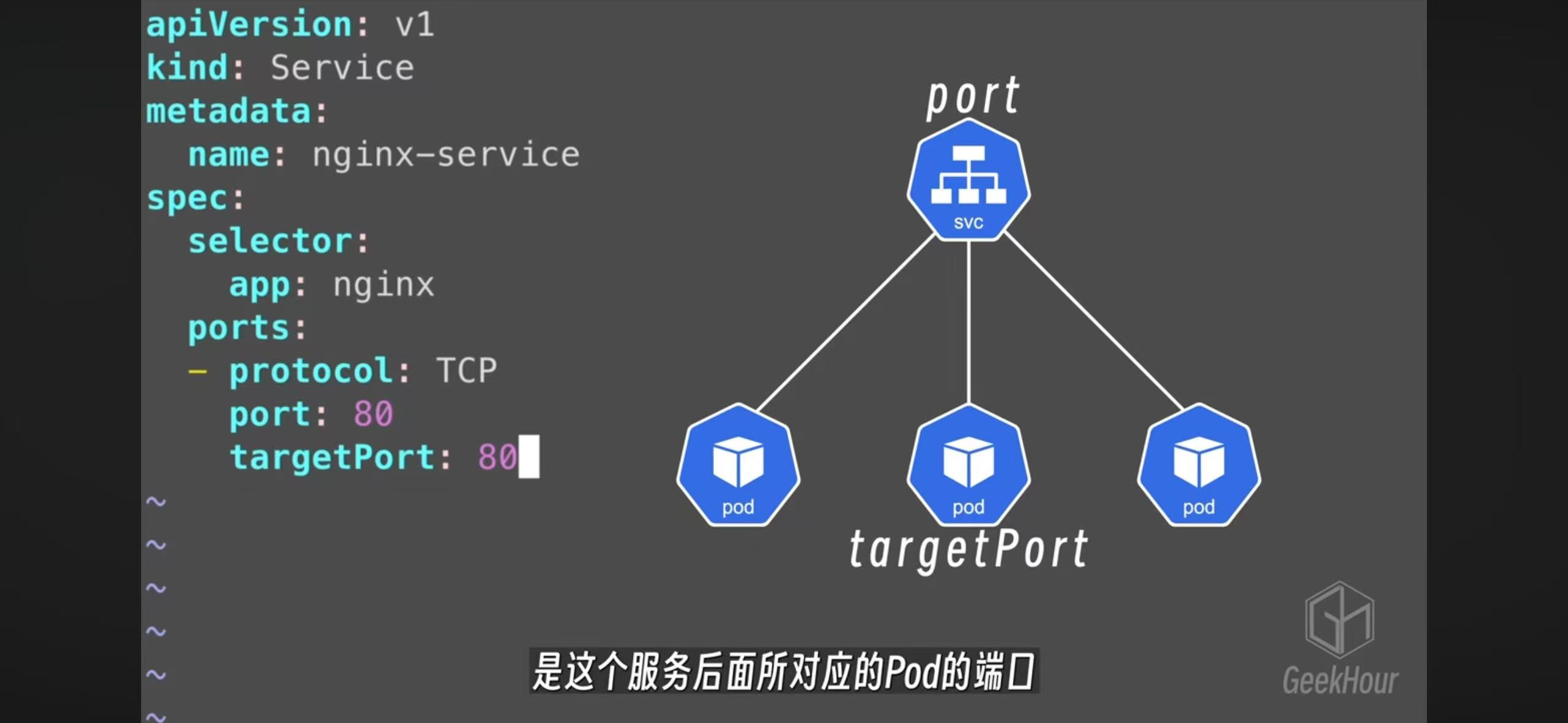
- The nodeport can map internal targetPort into external facing port
Here are list of other service type

- Port exposes the Kubernetes service on the specified port within the cluster. Other pods within the cluster can communicate with this server on the specified port.
- TargetPort is the port on which the service will send requests to, that your pod will be listening on. Your application in the container will need to be listening on this port also.
- NodePort exposes a service externally to the cluster by means of the target nodes IP address and the NodePort. NodePort is the default setting if the port field is not specified.
```yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: vllm-agg-router-frontend
namespace: dynamo-cloud
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
nvidia.com/selector: vllm-agg-router-frontend
ports:
- protocol: TCP port: 8000 # internally facing within k8s targetPort: 8000 # port application inside container nodePort: 30080 # port externally facing ```