Flow and Diffusion models Lab 2-2 - Gaussian Probability Path w Score matching
I separat the score matching part from the Lab 2 and all put into this blog. So we can see more clearly how it works
1 Score Matching using Conditional Scores
Analytically, the score function is defined as $\nabla_x \log p_t(x|z) = \nabla_x N(x;\alpha_t z,\beta_t^2 I_d) = \frac{\alpha_t z - x}{\beta_t^2}.$
class GaussianConditionalProbabilityPath(ConditionalProbabilityPath):
...
def conditional_score(self, x: torch.Tensor, z: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Evaluates the conditional score of p_t(x|z) = N(alpha_t * z, beta_t**2 * I_d)
Note: Only defined on t in [0,1)
Args:
- x: position variable (num_samples, dim)
- z: conditioning variable (num_samples, dim)
- t: time (num_samples, 1)
Returns:
- conditional_score: conditional score (num_samples, dim)
"""
alpha_t = self.alpha(t)
beta_t = self.beta(t)
return (z * alpha_t - x) / beta_t ** 2
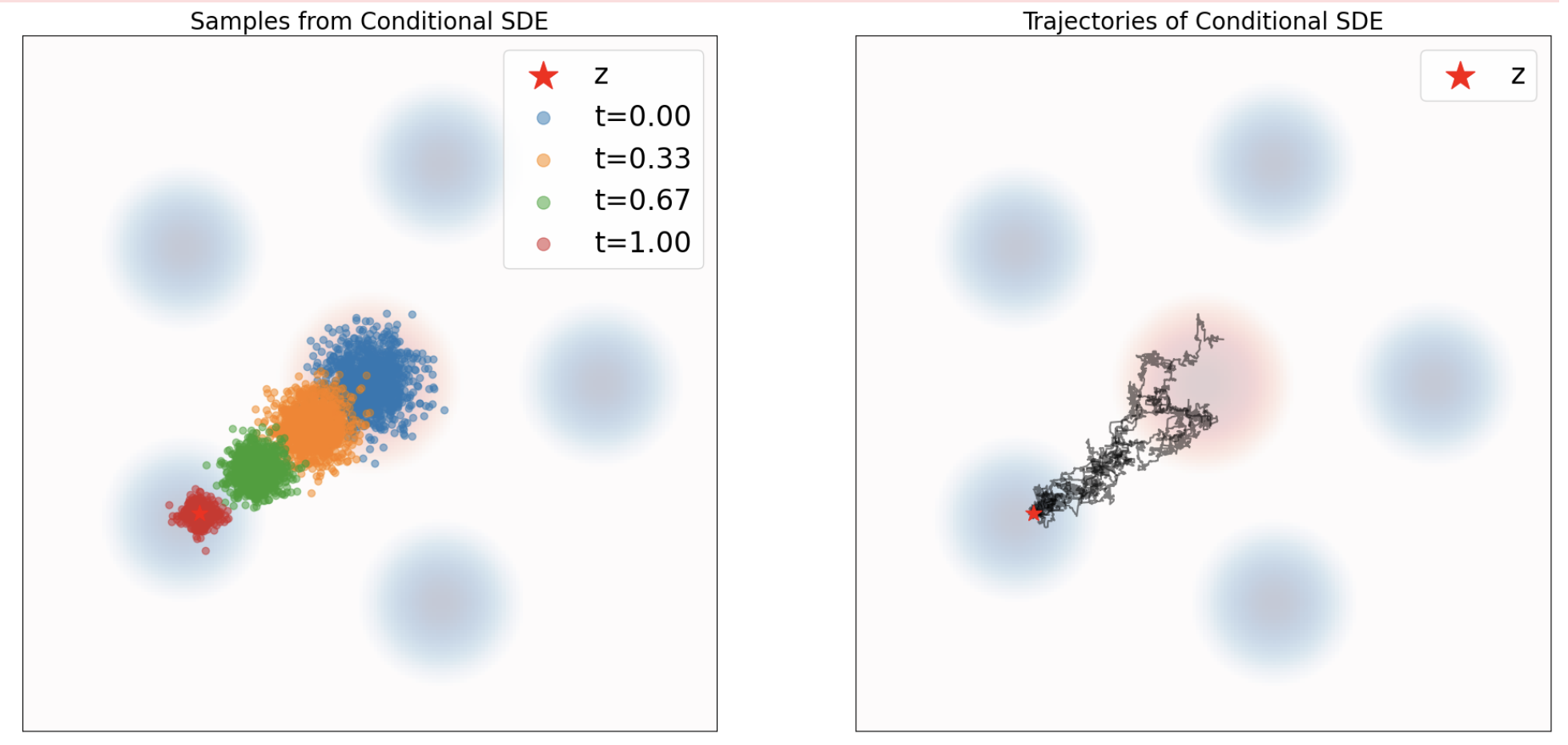
Define the SDE by adding Langevin Dynamics to the ODE function. \(d X_t = \left[u_t(X_t|z) + \frac{1}{2}\sigma^2 \nabla_x \log p_t(X_t|z) \right]dt + \sigma\, dW_t, \quad \quad X_0 = x_0 \sim p_{\text{simple}},\)
class ConditionalVectorFieldSDE(SDE):
def __init__(self, path: ConditionalProbabilityPath, z: torch.Tensor, sigma: float):
"""
Args:
- path: the ConditionalProbabilityPath object to which this vector field corresponds
- z: the conditioning variable, (1, ...)
"""
super().__init__()
self.path = path
self.z = z
self.sigma = sigma
def drift_coefficient(self, x: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
bs = x.shape[0]
z = self.z.expand(bs, *self.z.shape[1:])
return self.path.conditional_vector_field(x,z,t) + 0.5 * self.sigma**2 * self.path.conditional_score(x,z,t)
def diffusion_coefficient(self, x: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.sigma * torch.randn_like(x)
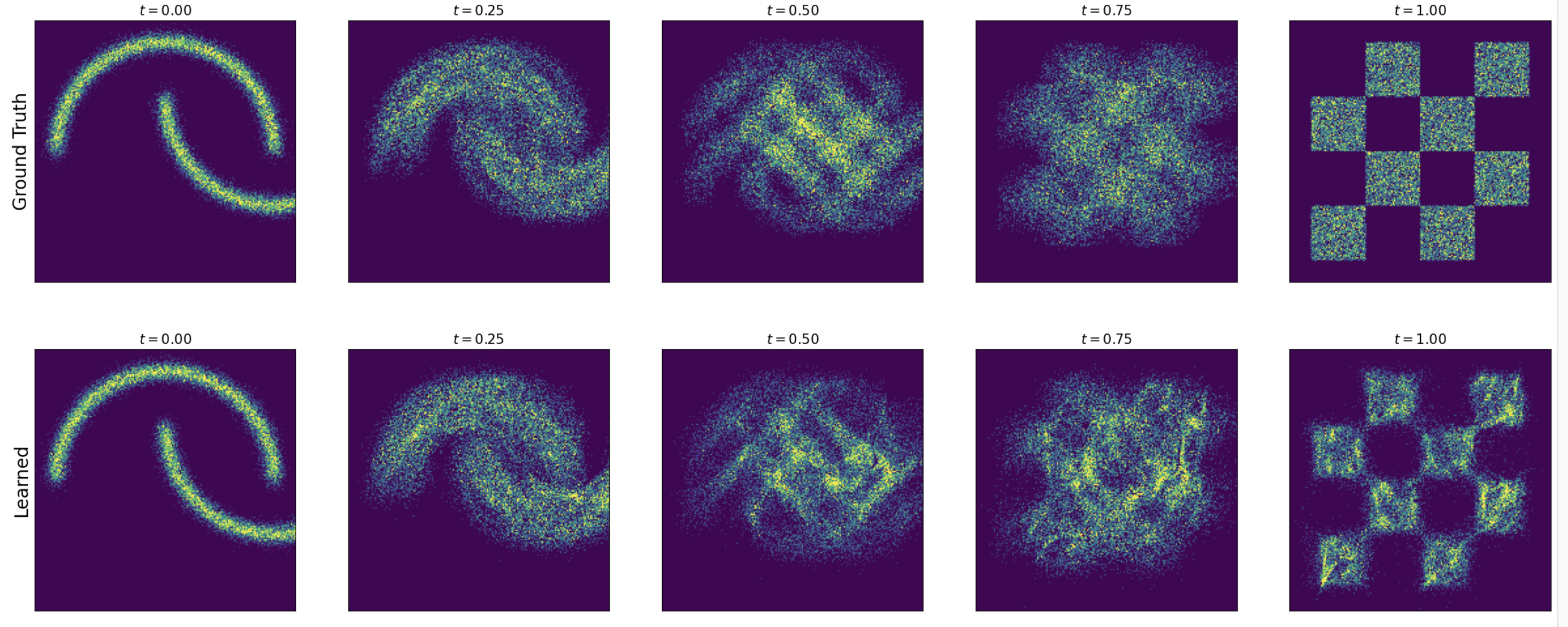
Now similar to ODE, you can plot every nth xts and all xts for trajectory
sde = ConditionalVectorFieldSDE(path, z, sigma)
simulator = EulerMaruyamaSimulator(sde)
x0 = path.p_simple.sample(num_samples) # (num_samples, 2)
ts = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num_timesteps).view(1,-1,1).expand(num_samples,-1,1).to(device) # (num_samples, nts, 1)
xts = simulator.simulate_with_trajectory(x0, ts) # (bs, nts, dim)
2 Training score matching
Similarly to flow matching, the loss based on marginal score matching is a constant plus loss of conditional score matching, so we can traing the marginal score based on the loss of conditional score. \(\mathcal{L}_{\text{CSM}}(\theta) \triangleq \mathbb{E}_{t \sim \mathcal{U}[0,1), z \sim p(z), x \sim p_t(x|z)} \left[\lVert s_t^{\theta}(x) - \nabla \log p_t(x|z)\rVert^2\right]\)
zis sampled fromp_datatis sampled fromtorch.randxis sampled frompath.sample_conditional_path(z, t), same as groundtruths_refis get fromself.path.conditional_score(x,z,t)class ConditionalScoreMatchingTrainer(Trainer): def __init__(self, path: ConditionalProbabilityPath, model: MLPScore, **kwargs): super().__init__(model, **kwargs) self.path = path def get_train_loss(self, batch_size: int) -> torch.Tensor: z = self.path.p_data.sample(batch_size) # (bs, dim) t = torch.rand(batch_size,1).to(z) # (bs, 1) x = self.path.sample_conditional_path(z,t) # (bs, dim) s_theta = self.model(x,t) # (bs, dim) s_ref = self.path.conditional_score(x,z,t) # (bs, dim) mse = torch.sum(torch.square(s_theta - s_ref), dim=-1) # (bs,) return torch.mean(mse)After the model is trained through MLP, generating a
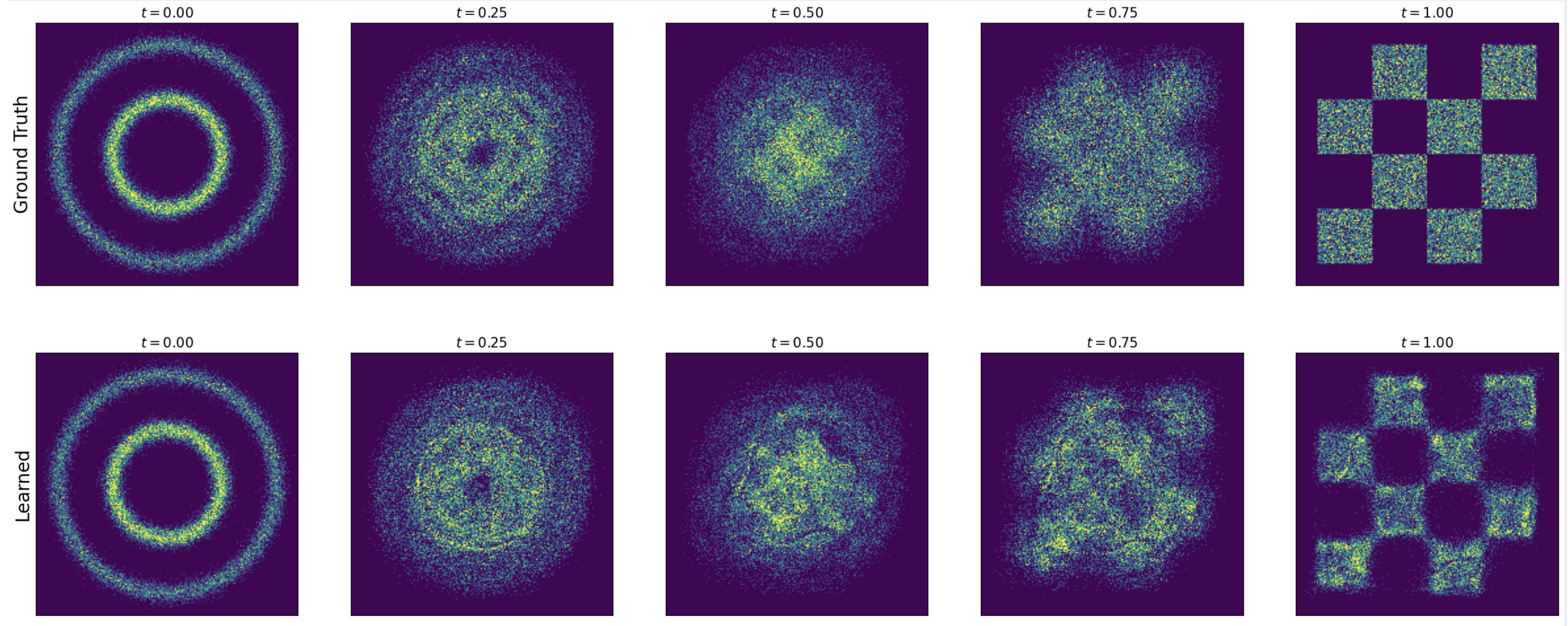
score_model, we can define the SDE together withflow_modelfrom ODE training.class LangevinFlowSDE(SDE): def __init__(self, flow_model: MLPVectorField, score_model: MLPScore, sigma: float): super().__init__() self.flow_model = flow_model self.score_model = score_model self.sigma = sigma def drift_coefficient(self, x: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor: return self.flow_model(x,t) + 0.5 * self.sigma ** 2 * self.score_model(x, t) def diffusion_coefficient(self, x: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor: return self.sigma * torch.randn_like(x)Here is how we get the marginal probability path
xts# Construct integrator and plot trajectories sde = LangevinFlowSDE(flow_model, score_model, sigma) simulator = EulerMaruyamaSimulator(sde) x0 = path.p_simple.sample(num_samples) # (num_samples, 2) ts = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num_timesteps).view(1,-1,1).expand(num_samples,-1,1).to(device) # (num_samples, nts, 1) xts = simulator.simulate_with_trajectory(x0, ts) # (bs, nts, dim)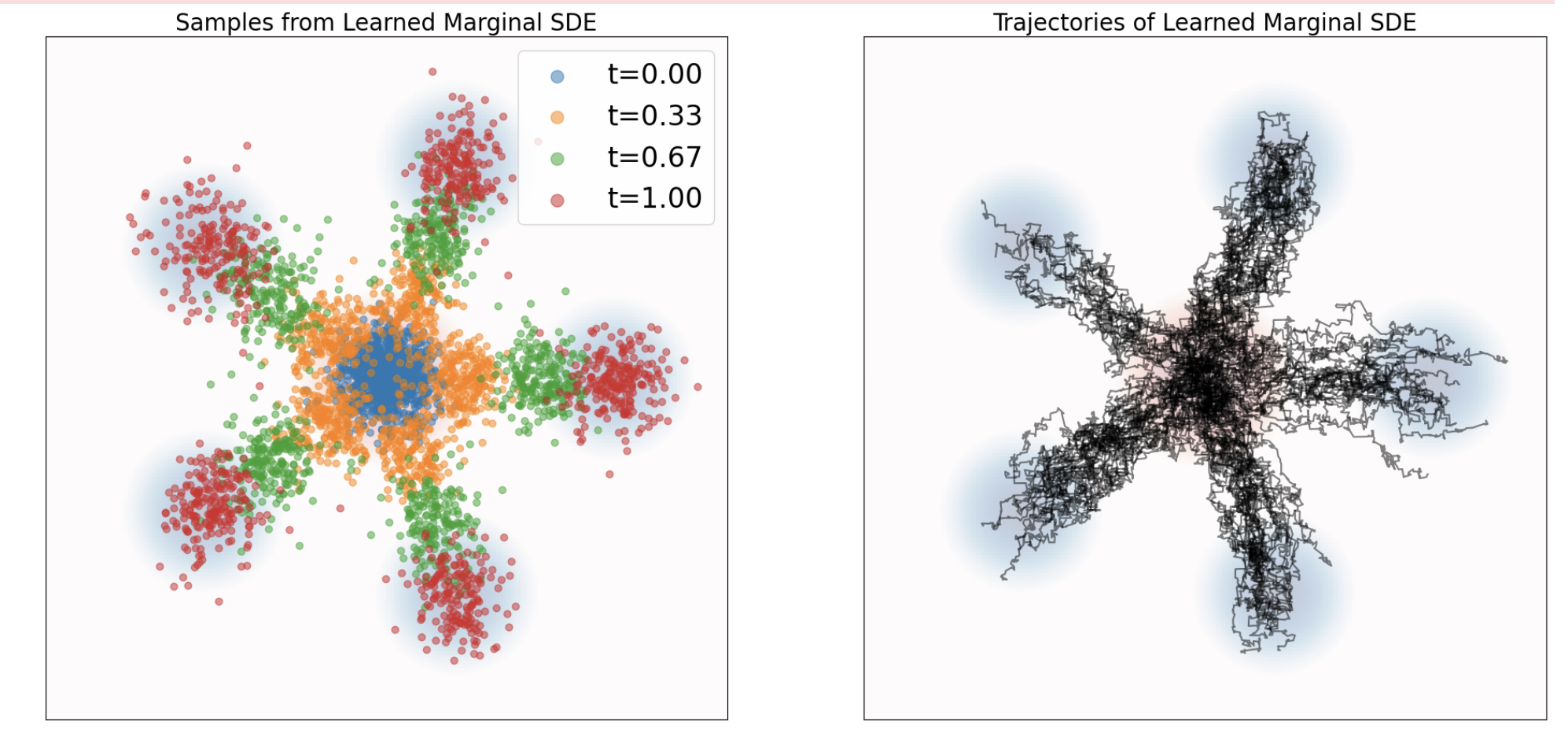
3 Get Score from Flow
Score can be calculated from Flow model, and implemented as below
class ScoreFromVectorField(torch.nn.Module):
"""
Parameterization of score via learned vector field (for the special case of a Gaussian conditional probability path)
"""
def __init__(self, vector_field: MLPVectorField, alpha: Alpha, beta: Beta):
super().__init__()
self.vector_field = vector_field
self.alpha = alpha
self.beta = beta
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor):
"""
Args:
- x: (bs, dim)
Returns:
- score: (bs, dim)
"""
alpha_t = self.alpha(t)
beta_t = self.beta(t)
dt_alpha_t = self.alpha.dt(t)
dt_beta_t = self.beta.dt(t)
num = alpha_t * self.vector_field(x,t) - dt_alpha_t * x
den = beta_t ** 2 * dt_alpha_t - alpha_t * dt_beta_t * beta_t
return num / den
4 Linear Probablity Path
At last, let’s try out a simple form of prabablity path, which does NOT require a guassian distribution for the $p_{init}$. But it does NOT have a closed form for the conditional score neither.
The linear path is given by a linear interpolation between $X_0$ and $z$.
\(X_t = (1-t) X_0 + tz\)
class LinearConditionalProbabilityPath(ConditionalProbabilityPath):
def __init__(self, p_simple: Sampleable, p_data: Sampleable):
super().__init__(p_simple, p_data)
def sample_conditioning_variable(self, num_samples: int) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.p_data.sample(num_samples)
def sample_conditional_path(self, z: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x0 = self.p_simple.sample(z.shape[0])
return (1 - t) * x0 + t * z
def conditional_vector_field(self, x: torch.Tensor, z: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return (z - x) / (1 - t)
def conditional_score(self, x: torch.Tensor, z: torch.Tensor, t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
raise Exception("You should not be calling this function!")
Here is the derivation of vector field
 Here you can
Here you can
- Graph conditional probability paths using
sample_conditional_pathas groundtruthxts = path.sample_conditional_path(zz, tt) - Graph conditional probability paths using `conditional_vector_field from ODE
ode = ConditionalVectorFieldODE(path, z) simulator = EulerSimulator(ode) ... x0 = path.p_simple.sample(num_samples) xts = simulator.simulate_with_trajectory(...) - Graph conditional probability paths using
sample_marginal_path:ts = path.sample_marginal_path(tt), which is actuallysample_conditional_pathwithnum_sampleof points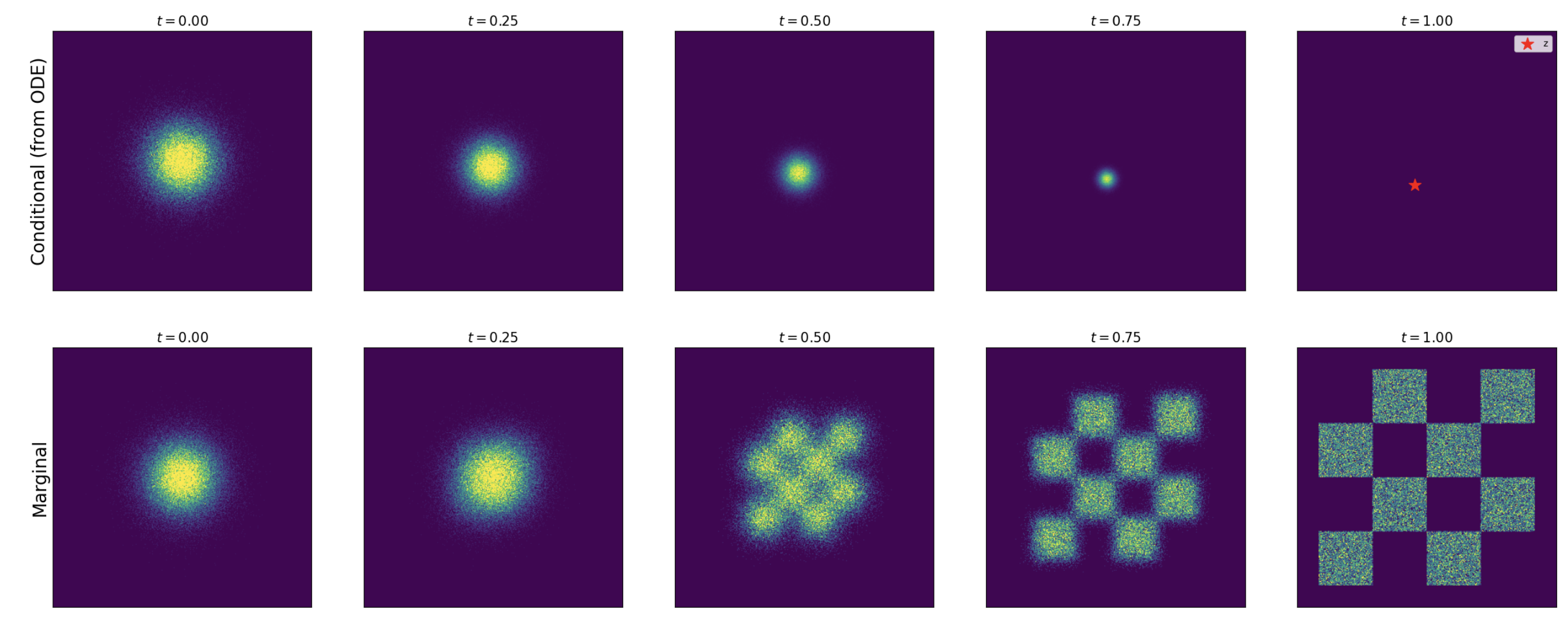
Arbitray $p_{init}$ can be used to get to $p_{data}$