vLLM parameters
To clarify meanings of some vLLM parameters
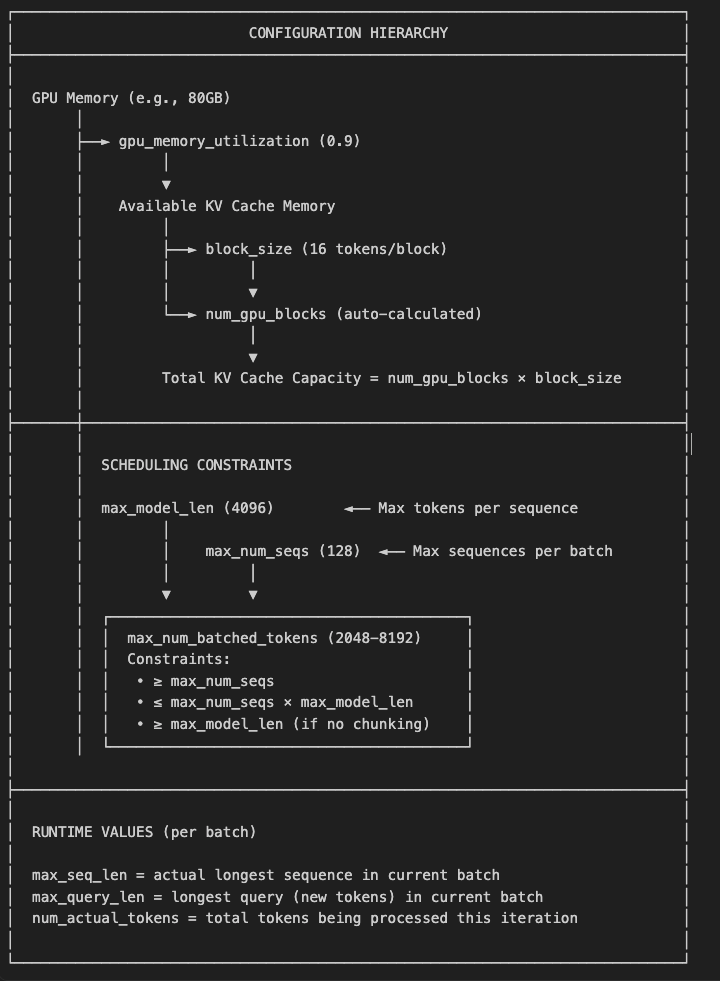
1. max_model_len (Configuration Parameter)
- This is a configuration setting defined in
ModelConfigthat specifies the maximum allowed context length (prompt + output) for the model.# model.pyLines 178-186 max_model_len: SkipValidation[int] = None # type: ignore """Model context length (prompt and output). If unspecified, will be automatically derived from the model config. When passing via `--max-model-len`, supports k/m/g/K/M/G in human-readable format. Examples:\n - 1k -> 1000\n - 1K -> 1024\n - 25.6k -> 25,600""" - Set via
--max-model-lenCLI argument or derived from the model’s HuggingFace config - Acts as an upper bound/limit for how long sequences can be Used for memory allocation planning and validation
- The default
max_model_lenis derived from the HuggingFace model config by checking these keys in order, and taking the smallest value found:
| Model Type | Config Key |
|---|---|
| LLaMA, Mistral, most modern models | max_position_embeddings |
| GPT-2 | n_positions |
| MPT | max_seq_len |
| ChatGLM | seq_length |
| Command-R, Cohere | model_max_length |
| Whisper | max_target_positions |
- Priority/Logic:
- Check all keys above → take the minimum value found across all of them
- Sliding window: If sliding window is disabled and the sliding window size is smaller, that becomes the limit
- Tokenizer config: model_max_length from tokenizer_config.json is also considered (takes the min)
- Fallback: If none of the keys are found, defaults to 2048 with a warning
2 max_seq_len (Runtime Value)
- This is a runtime metadata value used in the attention backends that represents the actual longest sequence length in the current batch being processed.
#utils.pyLines 77-80 max_query_len: int """Longest query in batch""" max_seq_len: int """Longest context length in batch""" - Computed dynamically for each batch: max_seq_len = seq_lens.max()
- Used by attention kernels to optimize memory access patterns
- Changes with every batch depending on the actual sequences being processed Key Difference.
| Aspect | max_model_len | max_seq_len | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Global config | Per-batch runtime | |
| Purpose | Upper bound/limit | Actual max in current batch | |
| When set | Server startup | Every inference step | |
| Value | Fixed (e.g., 4096) | Dynamic (≤ max_model_len) |
In short: max_model_len is the ceiling you configure, while max_seq_len is the actual maximum sequence length in the current batch being processed (always ≤ max_model_len).
3 max_num_seq(Configuration Parameter)
- Controls the maximum number of requests/sequences that can be batched together in a single forward pass.
#scheduler.py Lines 44-49 max_num_seqs: int = Field(default=DEFAULT_MAX_NUM_SEQS, ge=1) """Maximum number of sequences to be processed in a single iteration. The default value here is mainly for convenience when testing. In real usage, this should be set in `EngineArgs.create_engine_config`. """ -
Set via
--max-num-seqsCLI argument and default is 128 max_batch_sizeis not a separate config parameter and it’s typically just a local variable that’s set equal tomax_num_seqs.# __init__.py Line 46 max_batch_size = self.vllm_config.scheduler_config.max_num_seqs
4 max_num_batched_tokens
- Constraint:
max_num_batched_tokens>=max_num_seqsEach sequence needs at least 1 token, so you can’t have more sequences than tokens - Upper bound:
max_num_batched_tokens<=max_num_seqs*max_model_lenThe theoretical max tokens is when all sequences are at max length
5 Example batch
Seq 1: [tokens…] 150 tokens
Seq 2: [tokens…] 200 tokens
Seq 3: [tokens…] 300 tokens
…
Seq N: [tokens…]
Constraints:
- N ≤ 128 (
max_num_seqs) - Each seq ≤ 4096 tokens (
max_model_len) - Total tokens ≤ 8192 (
max_num_batched_tokens) - Actually longest sequence in current batch = 300 (
max_seq_len)# In gpu_model_runner.py max_seq_len = self.seq_lens.np[:num_reqs].max().item()