Claude Skills
I used to learn Skills, as the app for Alexa, which failed and no one is creating Alexa skills anymore. Anthropic started Skills concept again, which is a more advanced prompt engineer tools
Here is a good introduction from the first principles.
1 Overview
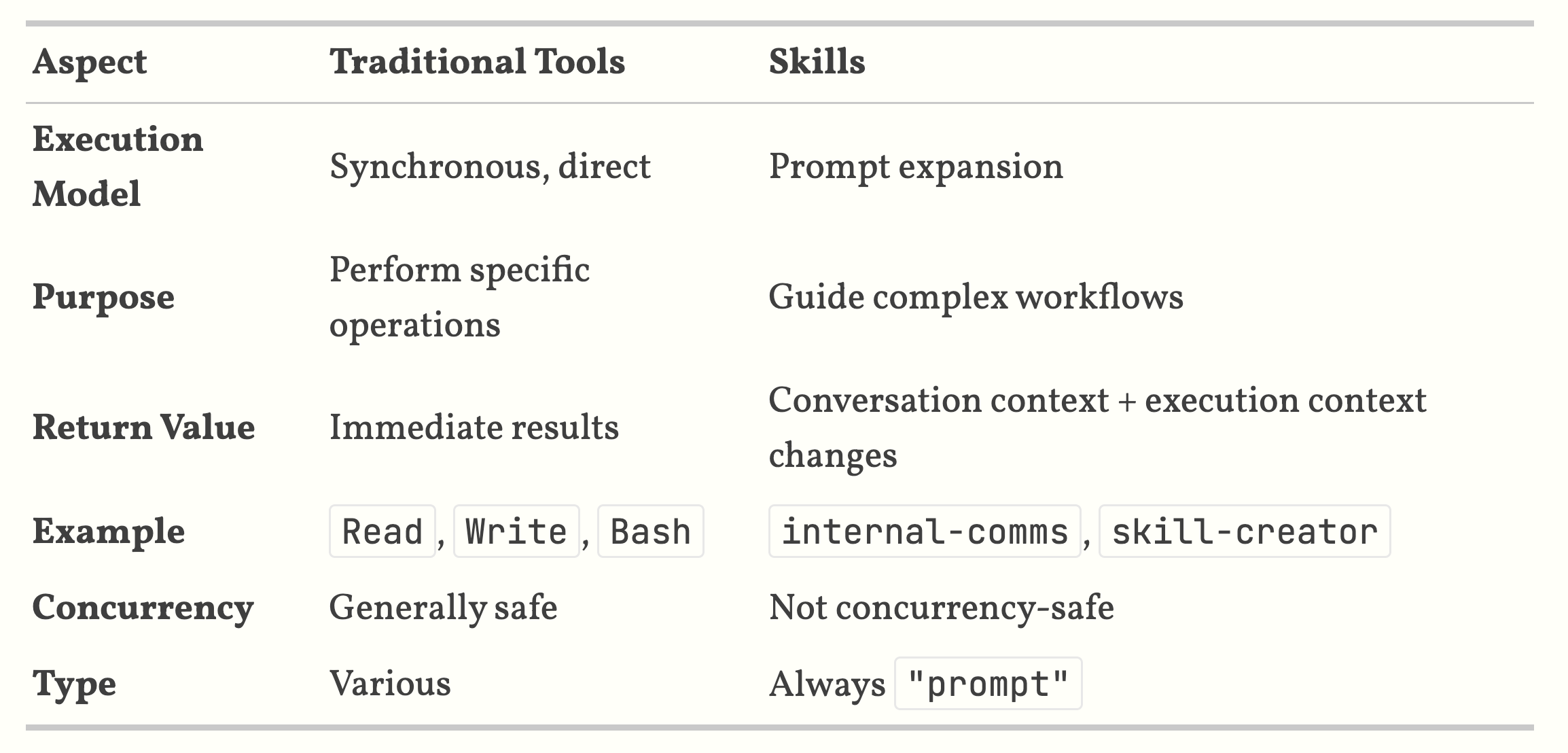
- Claude’s Agent Skills system represents a sophisticated prompt-based *meta-tool *architecture that extends LLM capabilities through specialized instruction injection.
- skills operate through prompt expansion and context modification to modify how Claude processes subsequent requests without writing executable code.
- There is no algorithmic skill selection. The decision-making happens entirely within Claude’s reasoning process based on the skill descriptions provided.
2 Skill structure
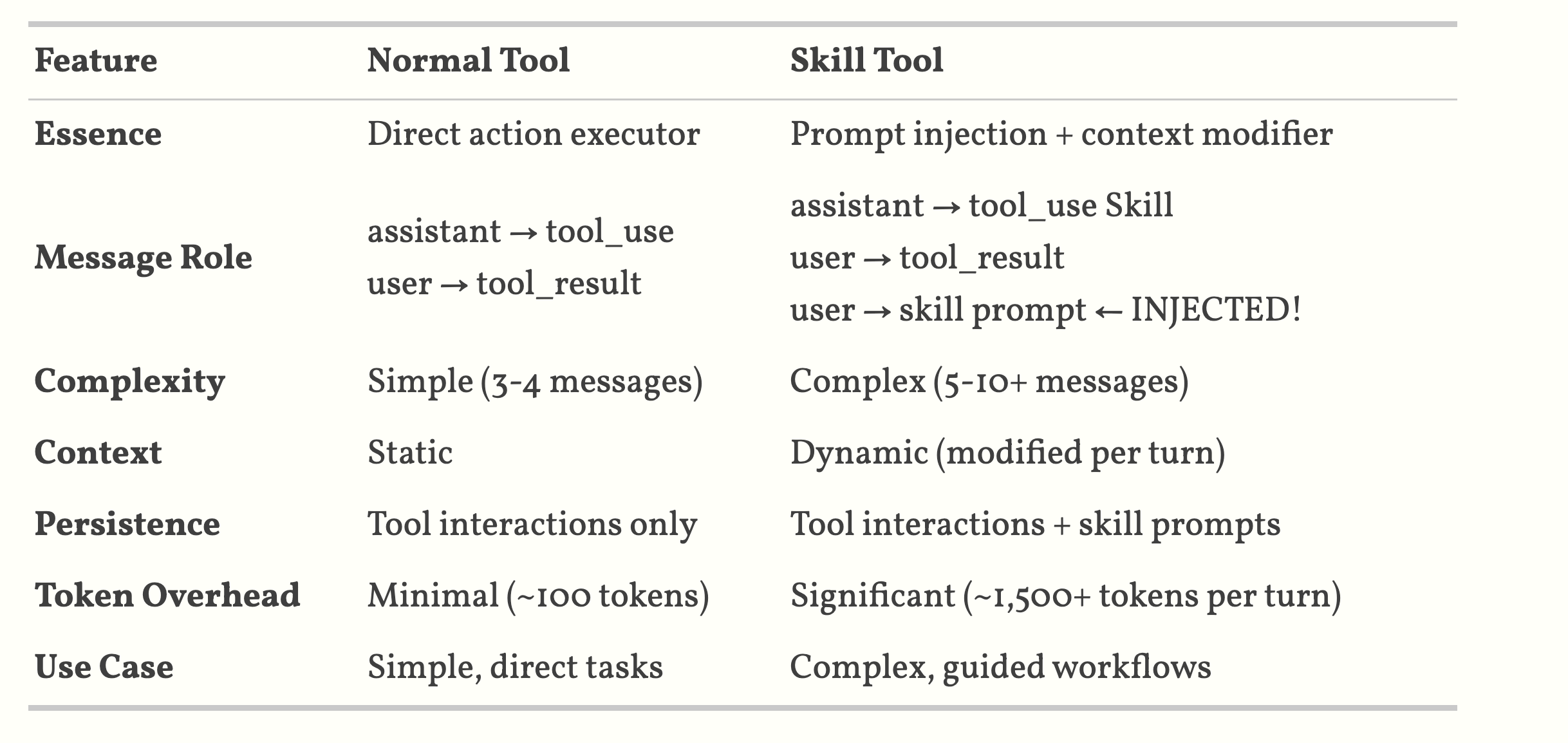
Skill = Prompt Template + Conversation Context Injection + Execution Context Modification + Optional data files and Python Scripts.
my-skill/ ├── SKILL.md # Core prompt and instructions ├── scripts/ # Executable Python/Bash scripts ├── references/ # Documentation loaded into context └── assets/ # Templates and binary files
Here is SKILL.md content
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. YAML Frontmatter (Metadata) │ ← Configuration
│ — │
│ name: skill-name │
│ description: Brief overview │
│ allowed-tools: “Bash, Read” │
│ version: 1.0.0 │
│ — │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 2. Markdown Content (Instructions) │ ← Prompt for Claude
│ │
│ Purpose explanation │
│ Detailed instructions │
│ Examples and guidelines │
│ Step-by-step procedures │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
3 Metadata
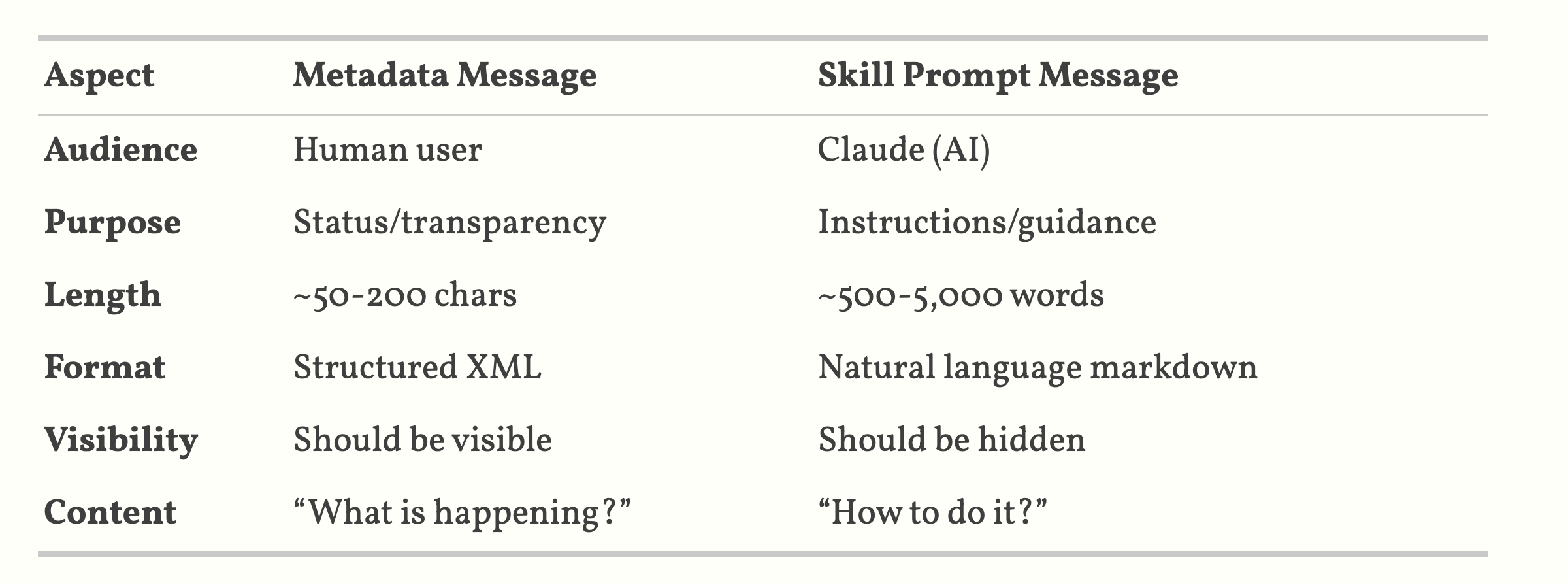
Two messages are injected, is_meta=False can be seen by users (default), otherwise meta data is only seen by API
4 Key Takeaways:
- Skills are prompt templates in SKILL.md files, not executable code
- The Skill tool (capital S) is a meta-tool in the tools array that manages individual skills, not in the system prompt
- Skills modify conversation context by injecting instruction prompts (via isMeta: true messages)
- Skills modify execution context by changing tool permissions and model selection Selection happens via LLM reasoning, not algorithmic matching
- Tool permissions are scoped to skill execution via execution context modification
- Skills inject two user messages per invocation— one for user-visible metadata, one for hidden instructions sent to the API