Disagg PD in vLLM and LMCache
Tested out Disagg PD in vLLM and sth about LMCache, an open-source Knowledge Delivery Network (KDN), and the Redis for LLMs.
1 Disagg PD in vLLM v0
Disagg PD in v0 is just a naive implementation using NCCL.
- It’s not fully integrate with vLLM serving, and a proxy server was used in the example to forward request from prefill to decode
- The proxy server can not handle genai-perf requests properly and no perf results were generated
- The serving is unstable, and it would exist after some torch distribution timeout
The serving script provided by vLLM basically does following things:
- starts two vLLM servings
- launches the proxy server.
- For prefill request, changes
max_tokensto be 1, and send request to prefill - Send the orginal request to decode.
2 LMCache PD in vLLM v1
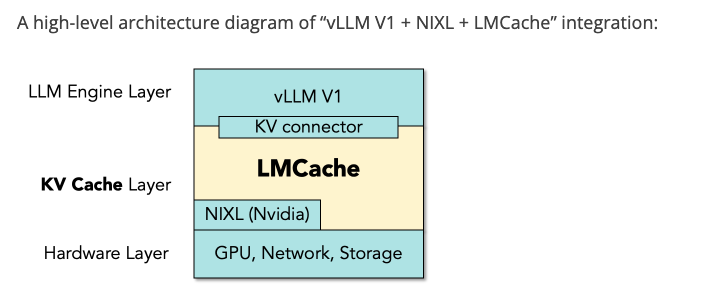
LMCache integrates with vLLM v1 and supports NIXL for ultra-fast KV cache transfer. Details in this blog and benchmark in this blog
 Key takeaways:
Key takeaways:
- LMCache batches the KV blocks into a single large buffe
- Smaller blocker (default 16 tokens), leads to many tiny transfers and underutilizing network
- Larger blockers, reduces prefix caching hit rates, and fragment GPU mem (opposite of paged attention philosophy)
- LMCache decoupled buffering step solves this issue.
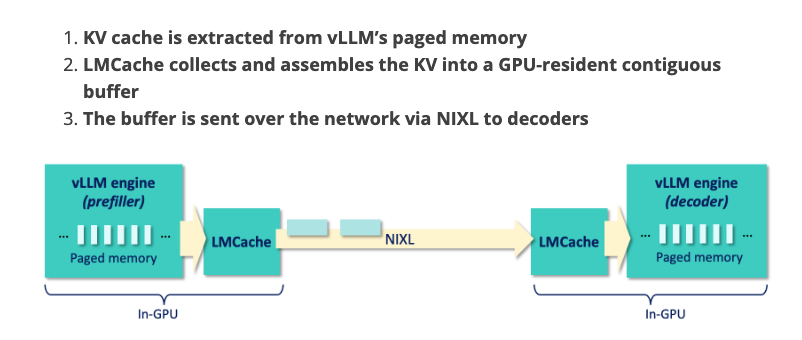 Detailed steps are listed in LMCache doc
Detailed steps are listed in LMCache doc