Reinforcement Learning - Policy Gradient
Learning RL is actually my very first ML project since joined AWS. DeepRace was released at reInvent 2018, and our prototype team got hand on it at early 2019. The task is straighforward: we are gonna do a hackathon with DeepRacer with one of the largest manufactory customer, and MS will be there as well. So the demo and contents needs to be shining and impressive.
So, here we go, Q-learning, Bellman equation, DQN, PPO, and …oh, it’s actually the first time I know a libary called Ray, which RLlib was used in the DeepRacer training source code
Here are some notes I took from review RL from Dr Hongyi Lee’s course:
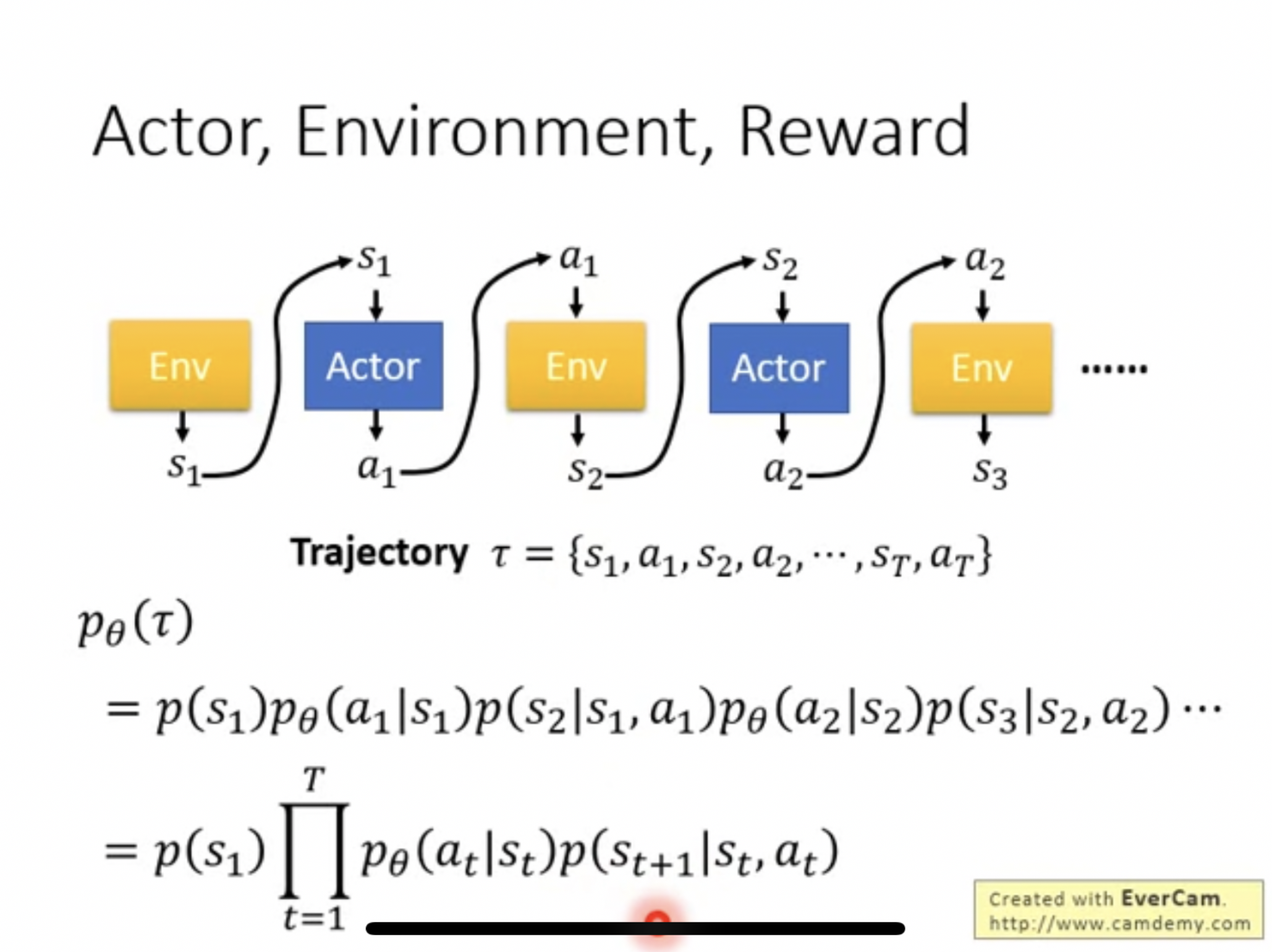
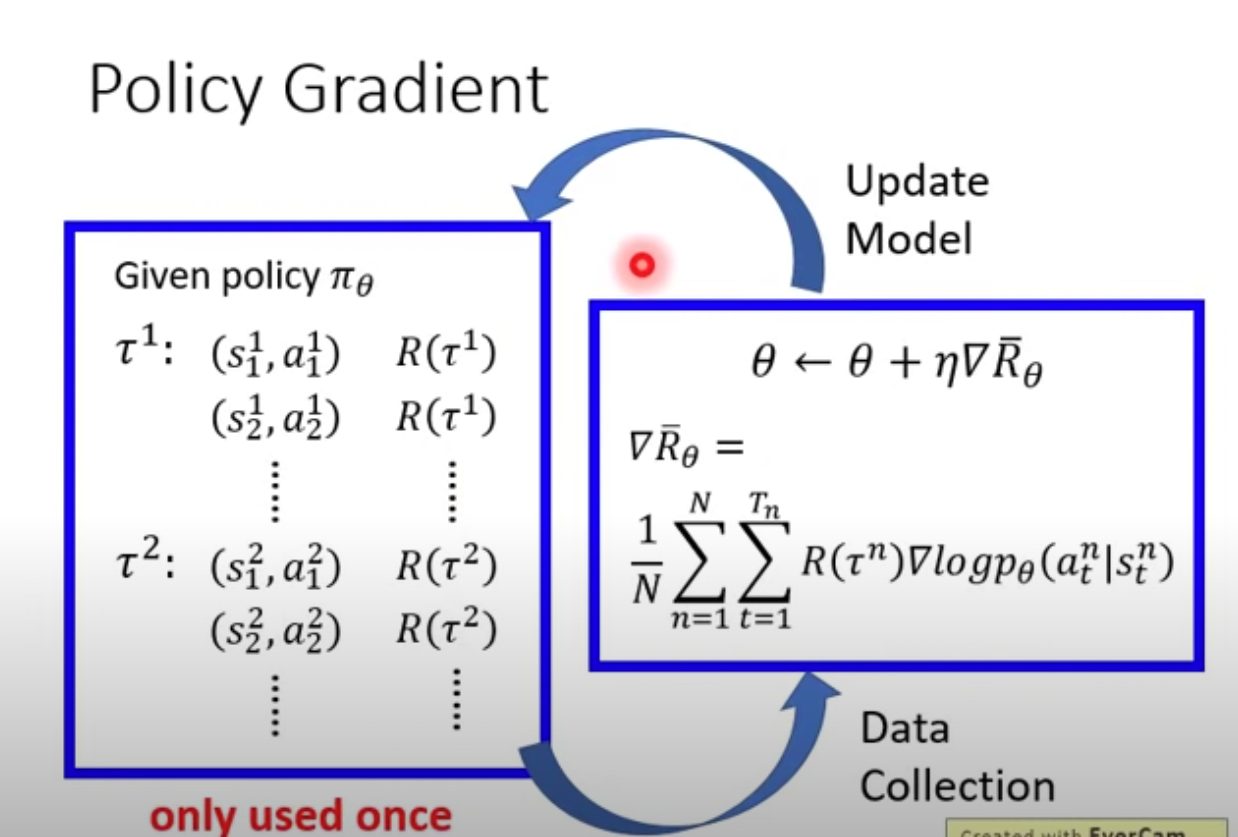
- Trajectory is combine of {states and actions}, and probability of a tracjectory under a defined policy, which parametered by $\theta$, can be calculated as follow
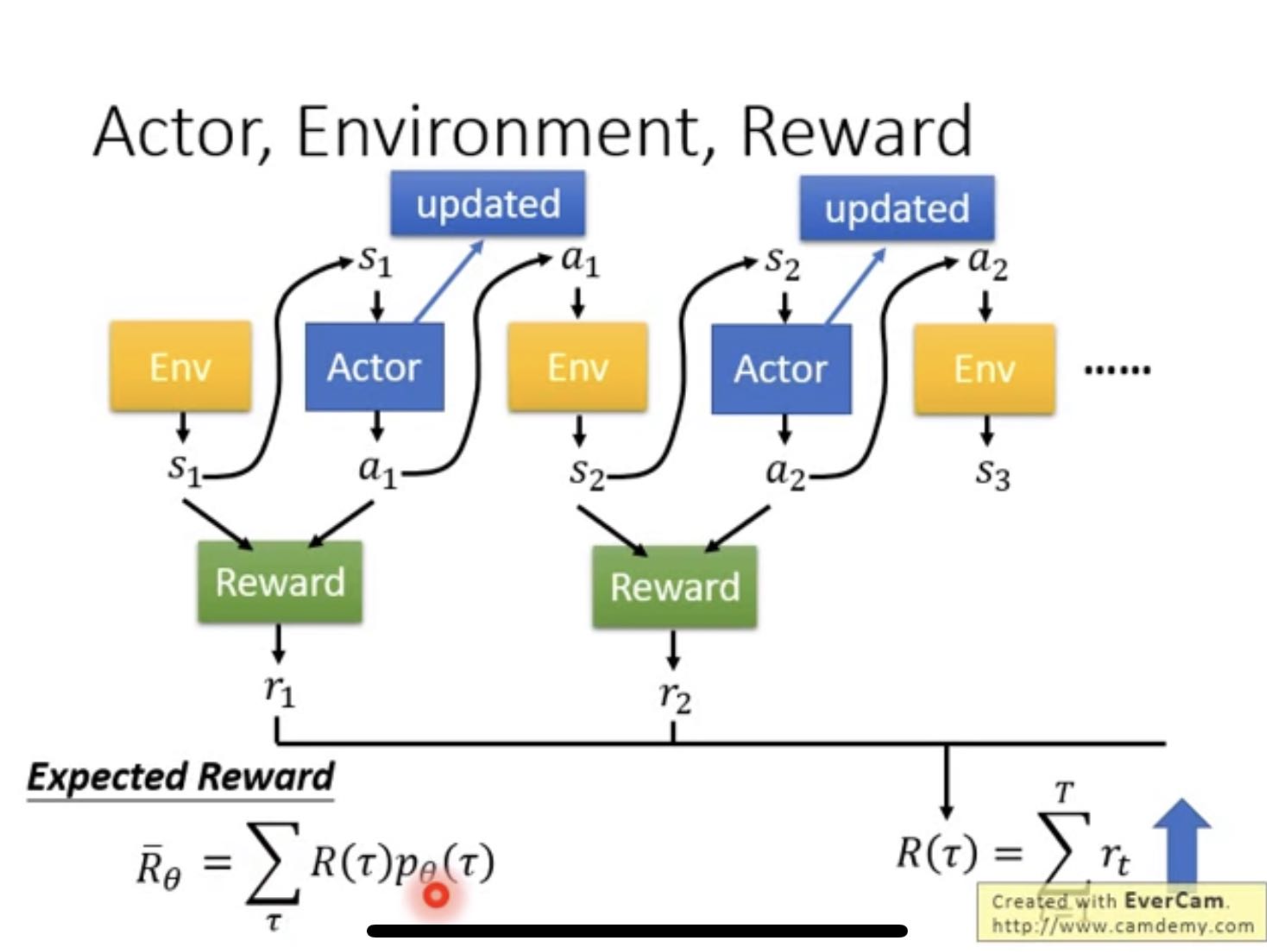
- Expected reward can be calculated with accumulated reward, weighted by prob. of trajectory
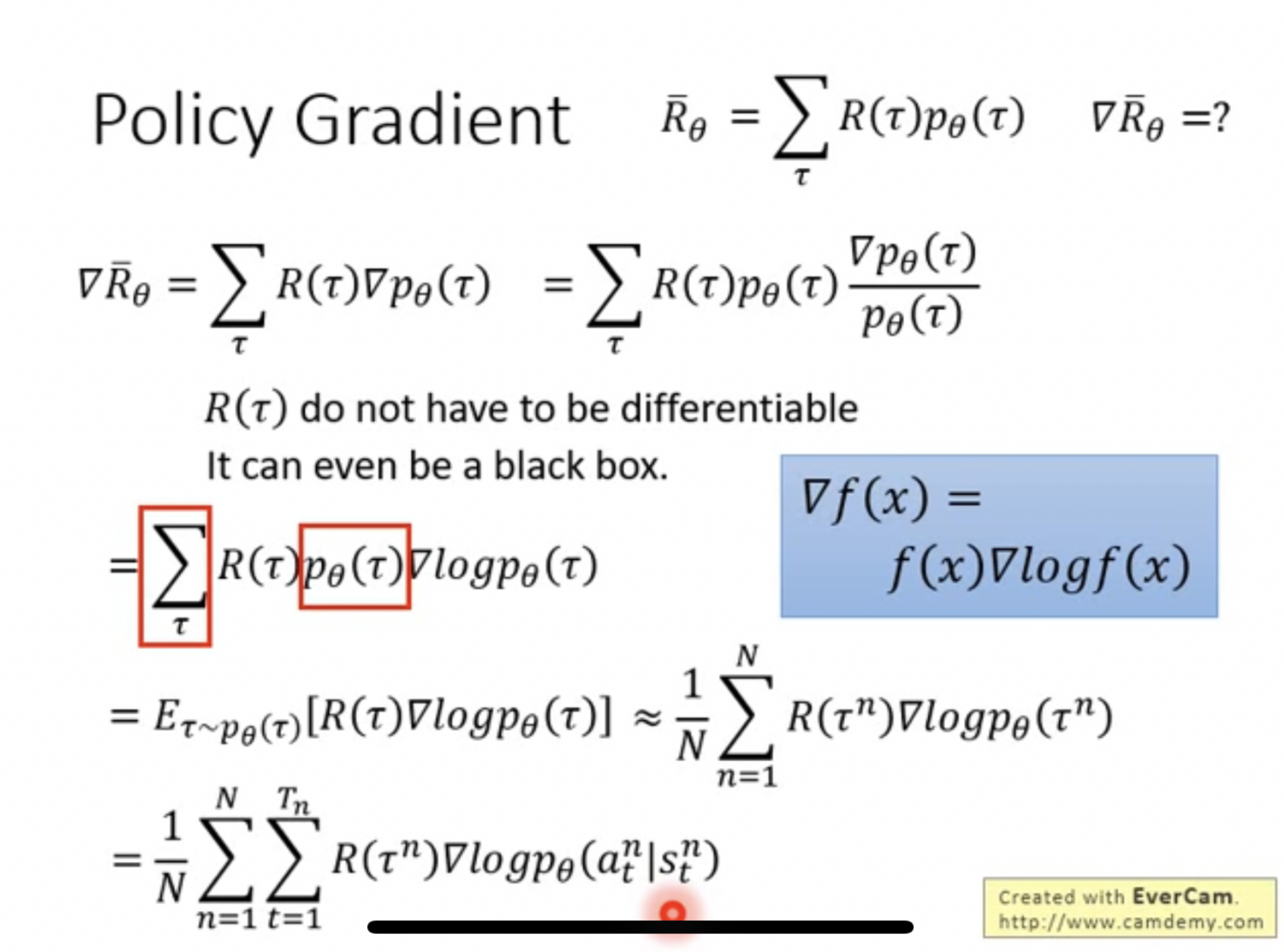
- Policy Gradient is taking gradient over the expected reward. Doing some math tricks to move $P_\theta(\tau)$ into a log and a rough estimation of expected value by sampling
- During implementations, you need to get states and actions
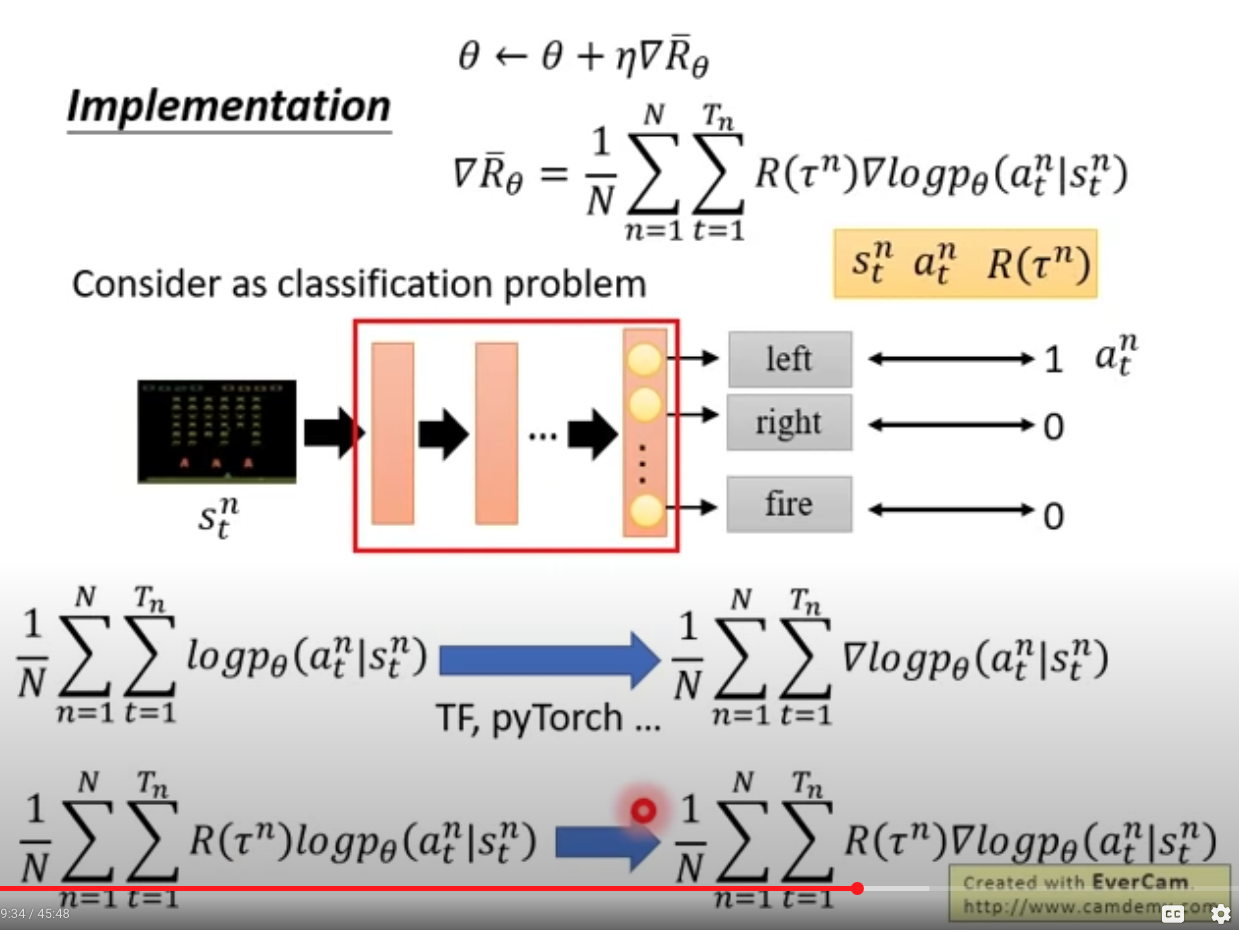
- Consider it as classification problem, so minimized cross-entropy, is essentially maximize likelihood, so in RL, we just weighted the likelihood by expected reward for the whole episode.
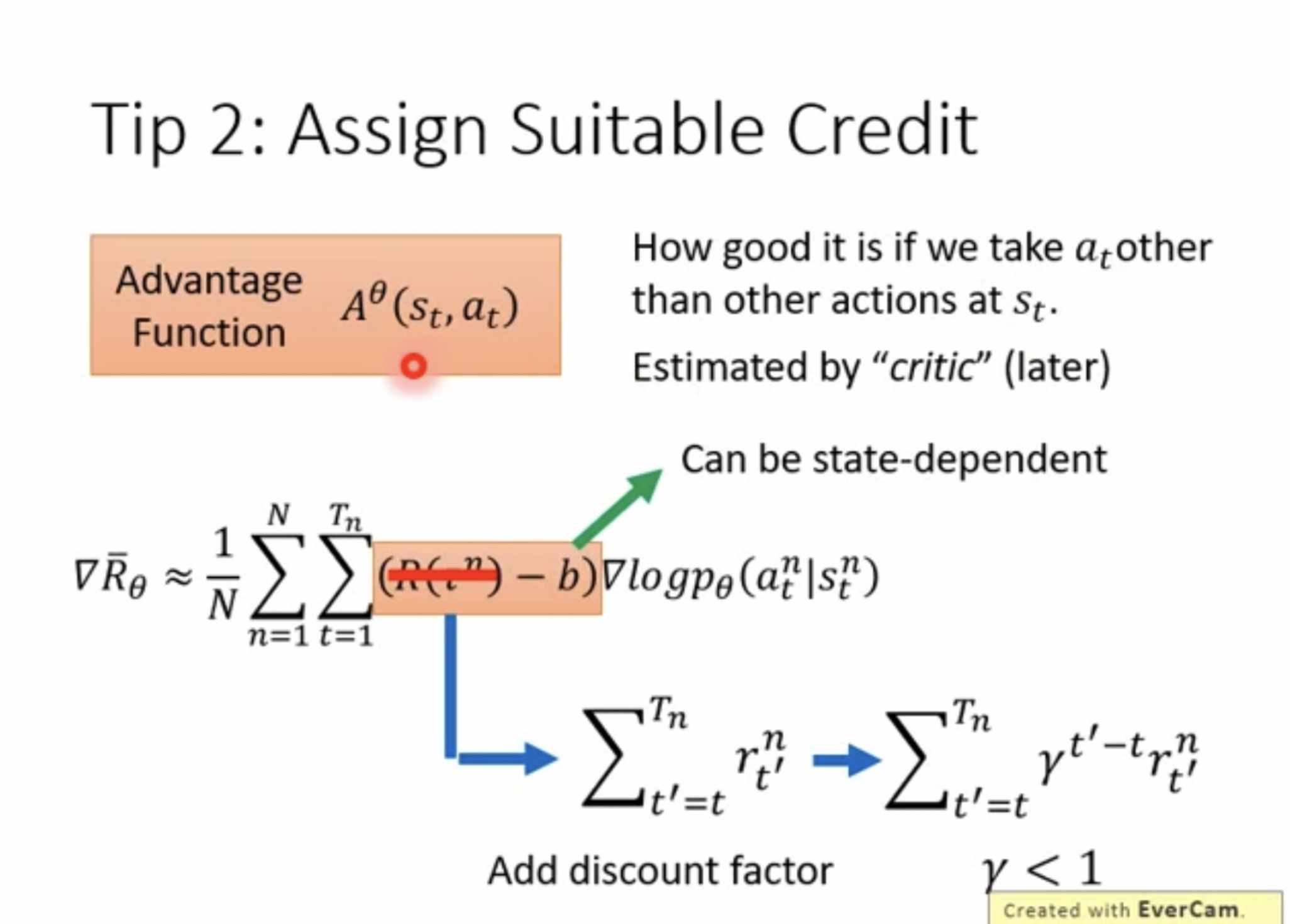
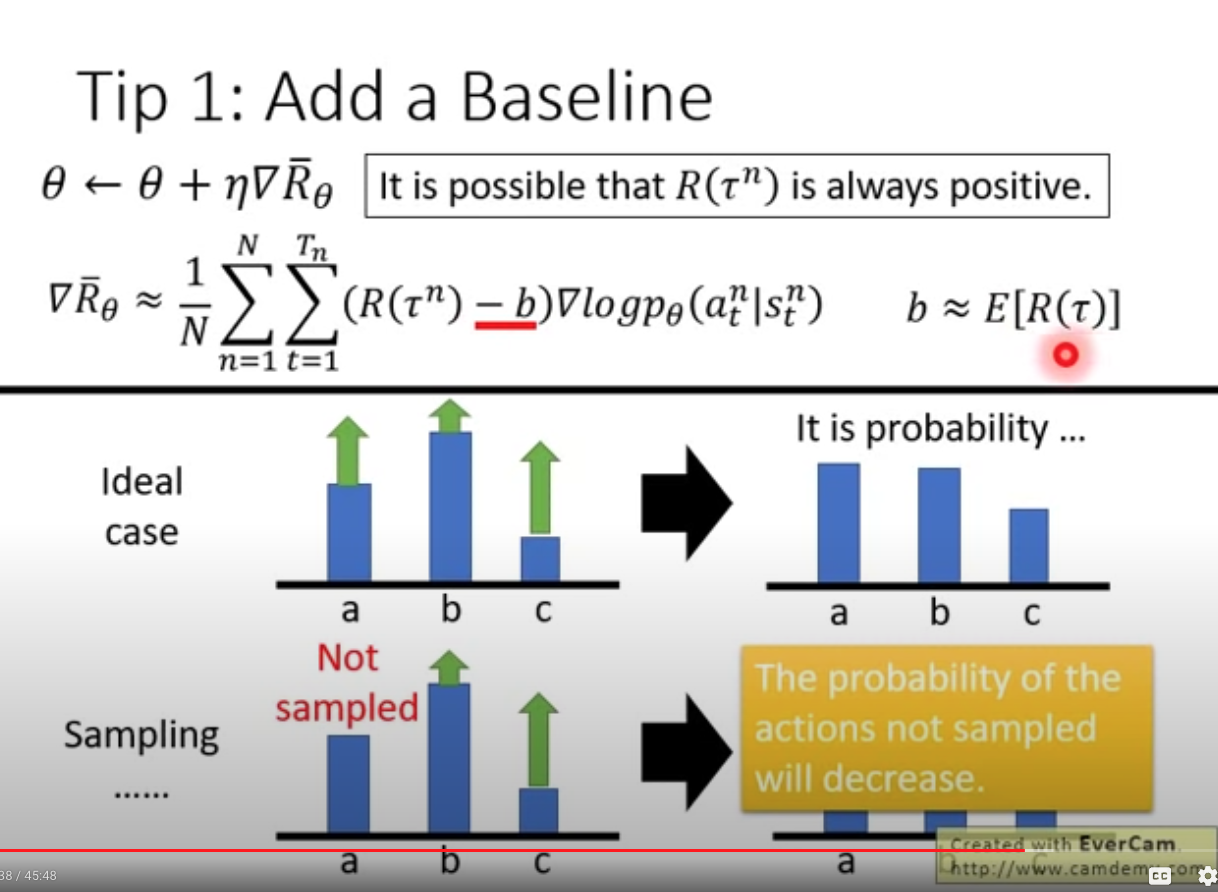
- Tip 1, add a basedline to avoid reward always be positive , so that non-sampled action will NOT stay constant.
- Tip 2, only consider rewards from $t$ time on (ignore actions early on), and adding discount factor $\gamma$. Thus we can define advantage function