K8S again
A k8s intro in Chinese from this video. It explains k8s concepts in a much clear way and I finally feel that I understand the architecture of k8s
1 Services
Let’s review ks8 components again
-
Pod Pod can have one or more containers. The best practice is one, and others are called side cars
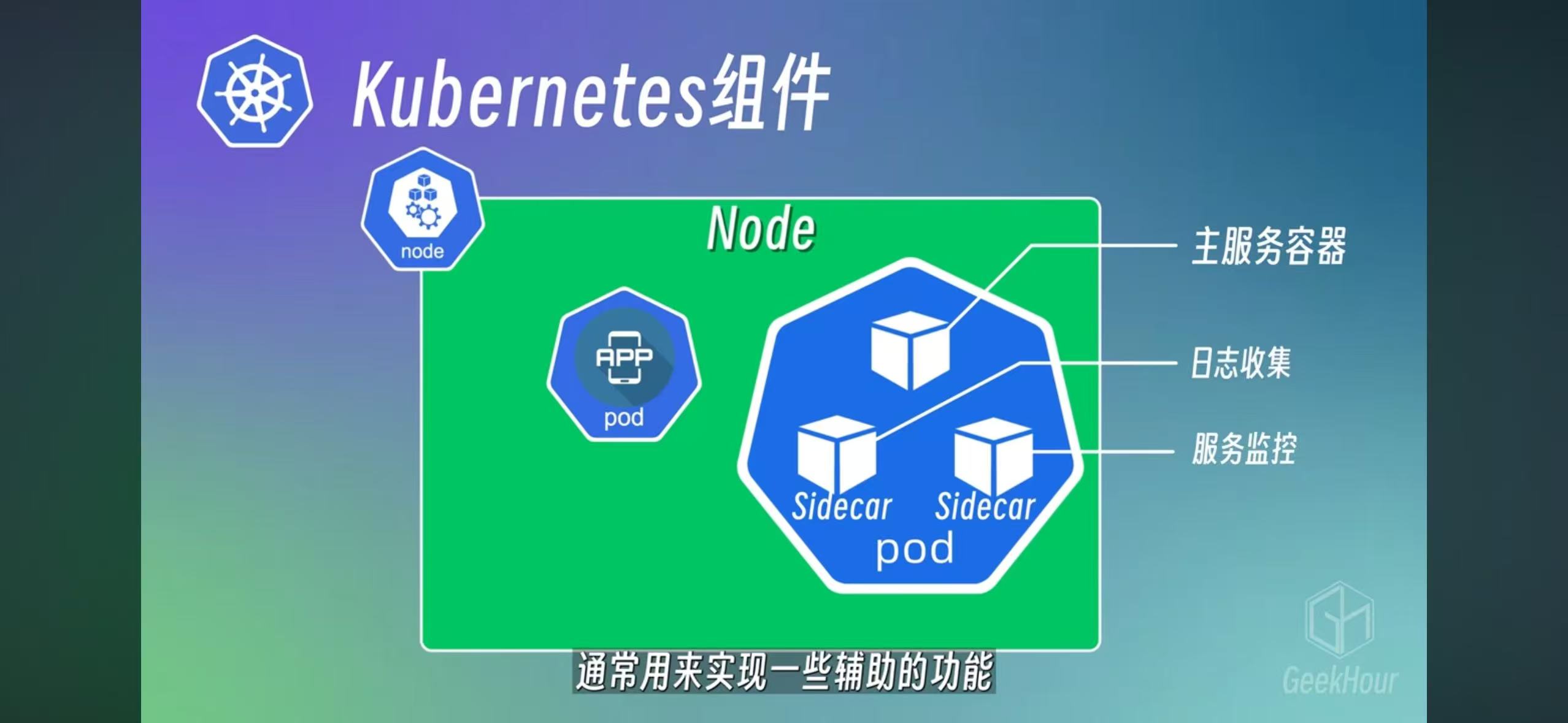
-
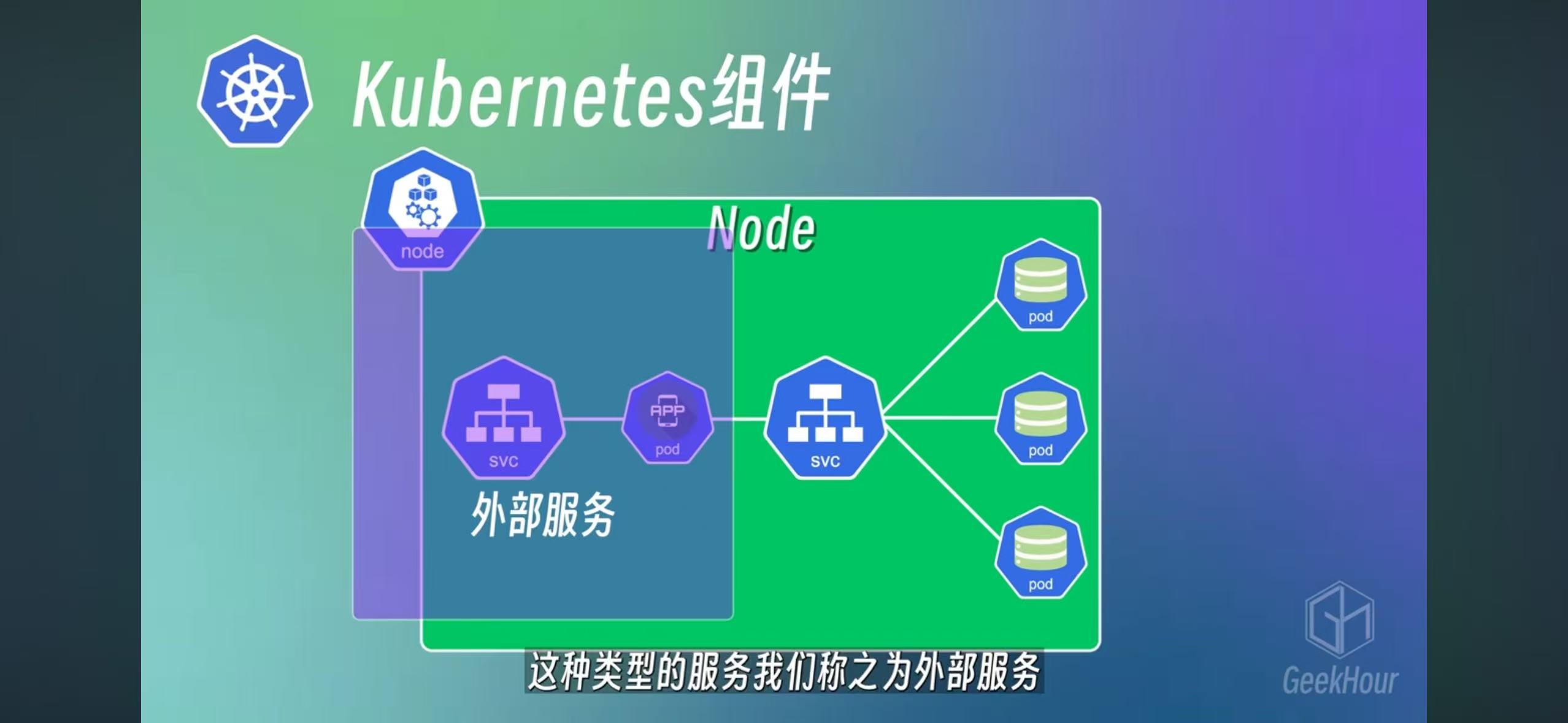
Service and NodePort Pod’s interal IP may change, so create a service can have fixed access to pod. and nodeport can be used for external access with a external facing port number.
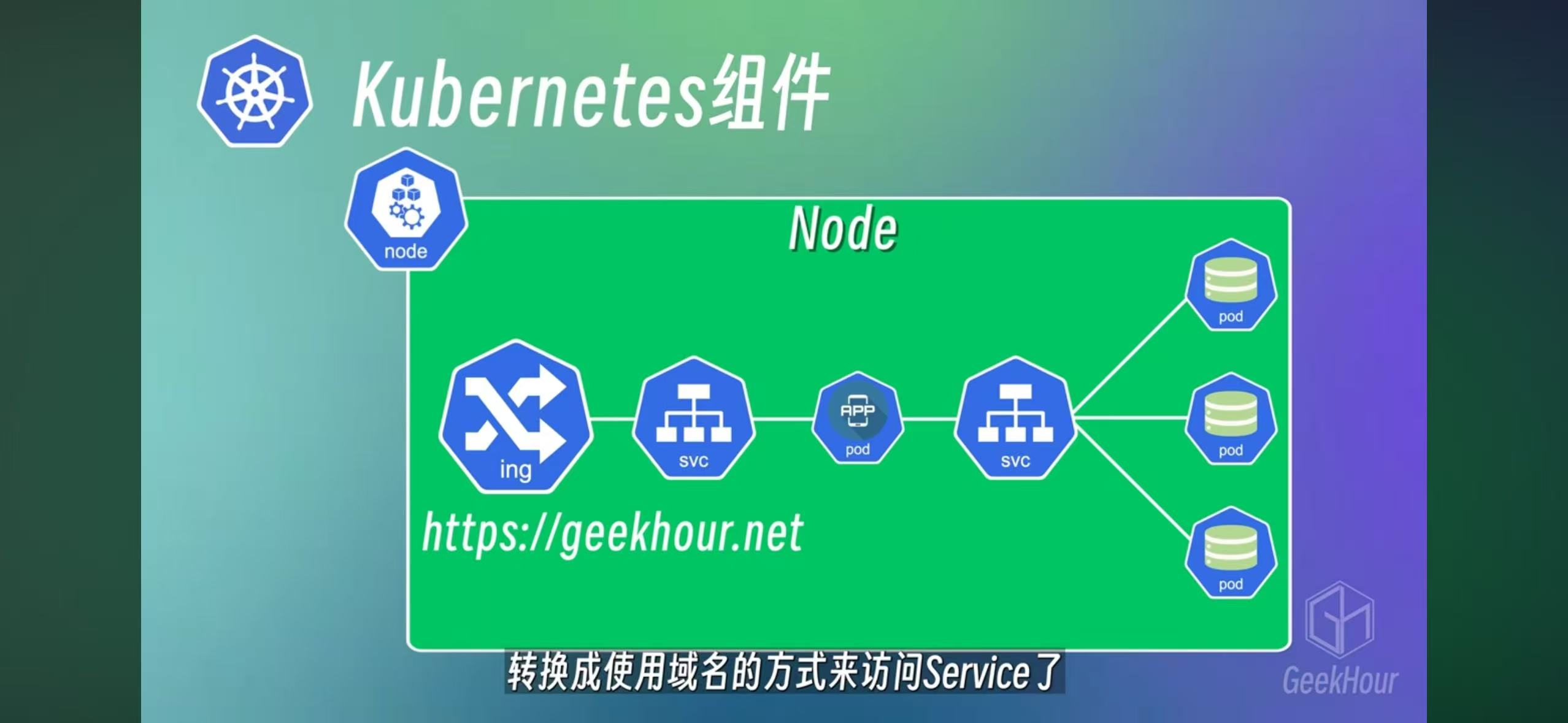
– Ingress
Ing is for external URL access
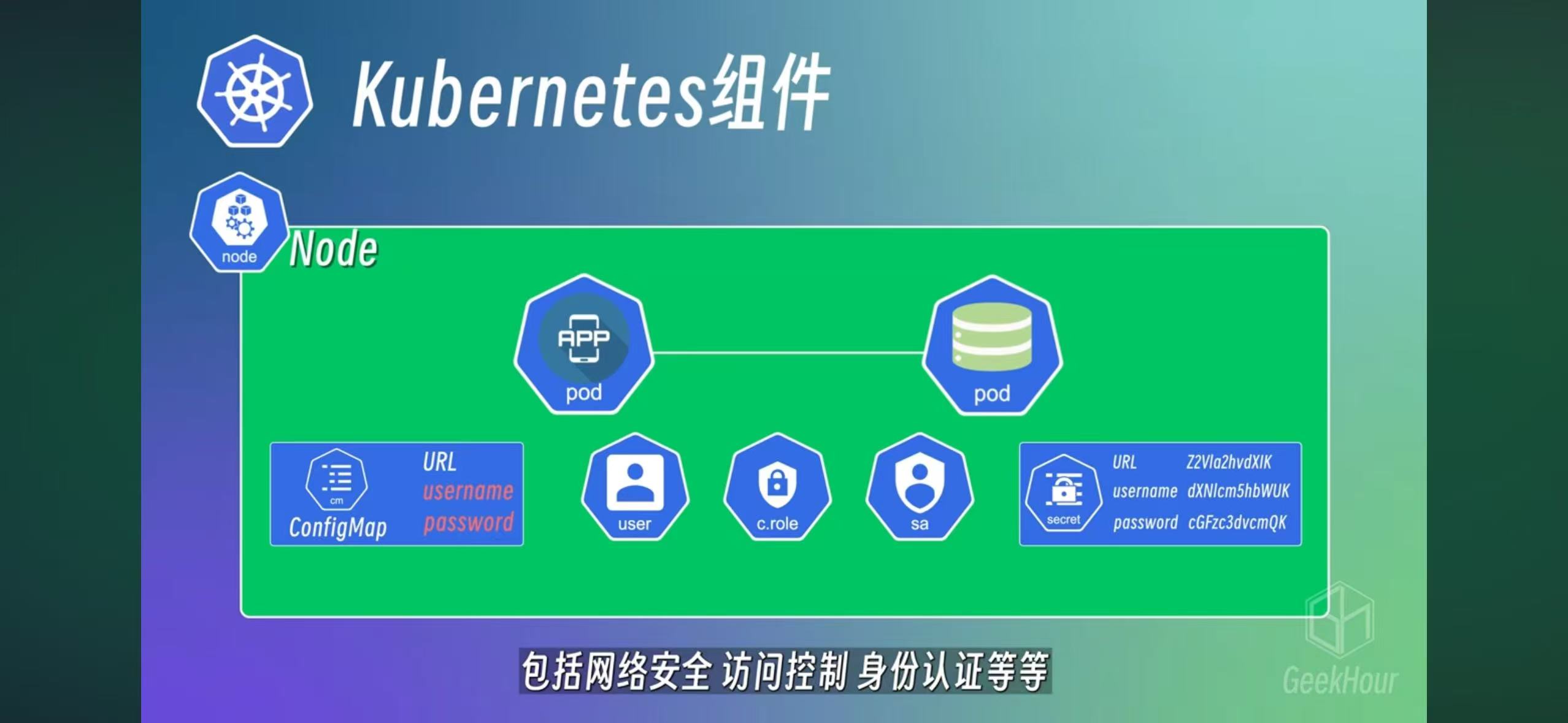
– ConfigMap and Secrets
Both are used to record config data. Secrets used base64 encoding, so it’s not really secret
– Deployment
A group of pods can be deployed by a deployment. and ReplicaSet is between pod and deployment
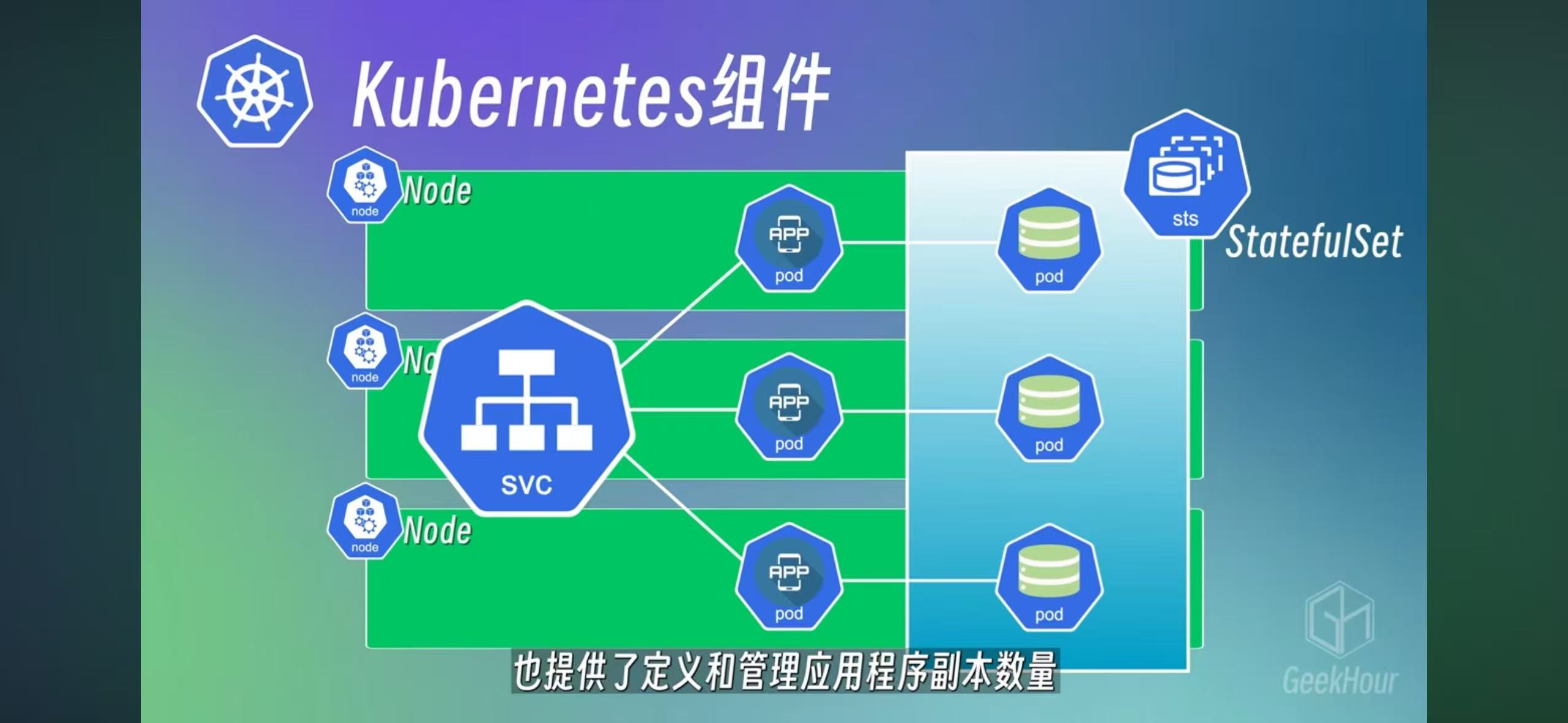
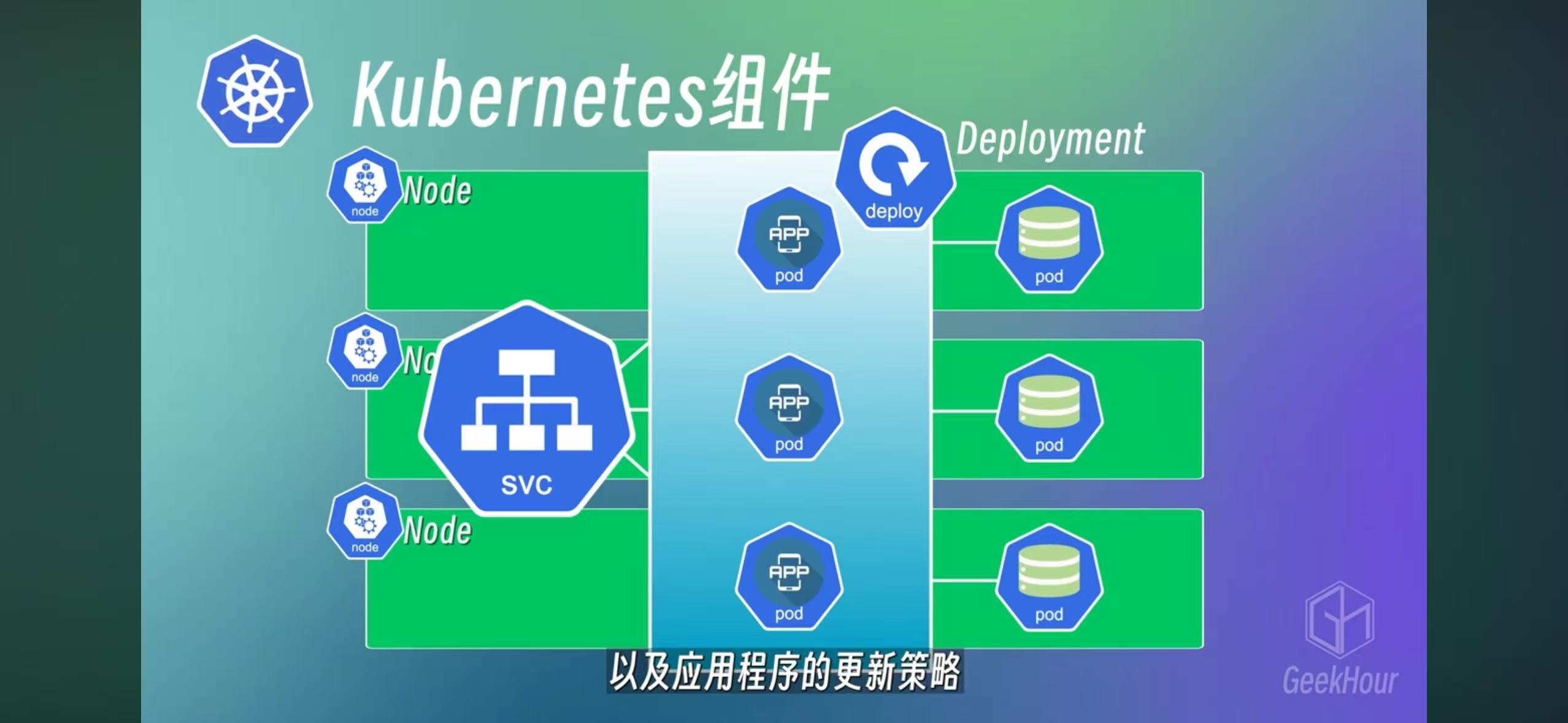 Statefulset is a deployment for database
Statefulset is a deployment for database
2 Master and Worker nodes
A worker has kubelet, kube-proxy(for networking), and a container runtime
 Master is build around APIServer to interact with kubectrl command
Master is build around APIServer to interact with kubectrl command
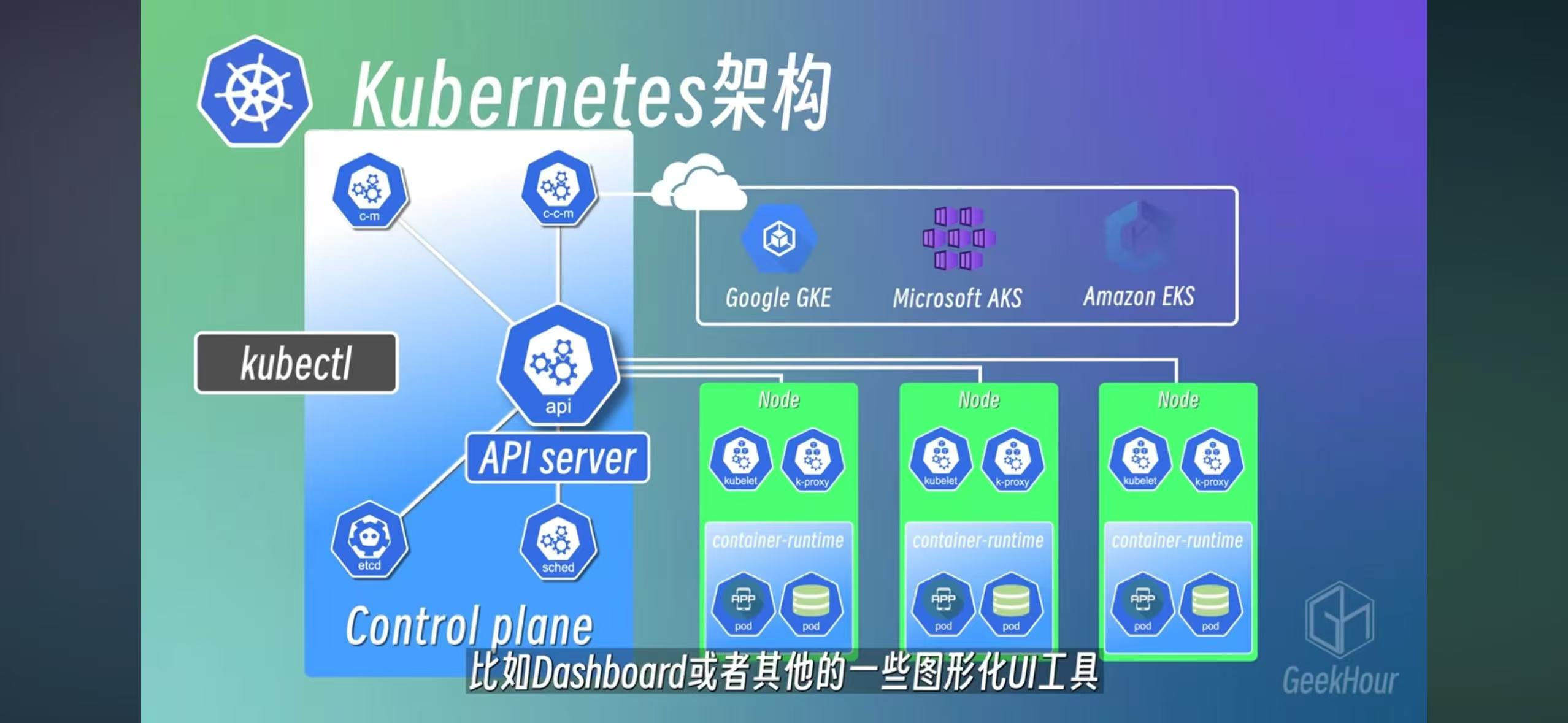
- API Server: Gateway to the k8s
- Scheduler: monitor resource usage for all services, assign pod into node
- c-m: Control Mangaer, check resource status
- etcd: Key-value storeage, similar to redis. It’s the brain of k8s and record all data for k8s
- c-c-m: Cloud-control-Manager, for connecting with EKS/AKS/GKS
3 K8S setup
- minukube: Creating a single node K8s
- multipass + k3s: A mini VM ware + mutile node k8s
- killacoda: online k8s sandbox
4 Examples
- The best practice of creating a pod is by creating a deployment. A replicaset will be create and also a pod
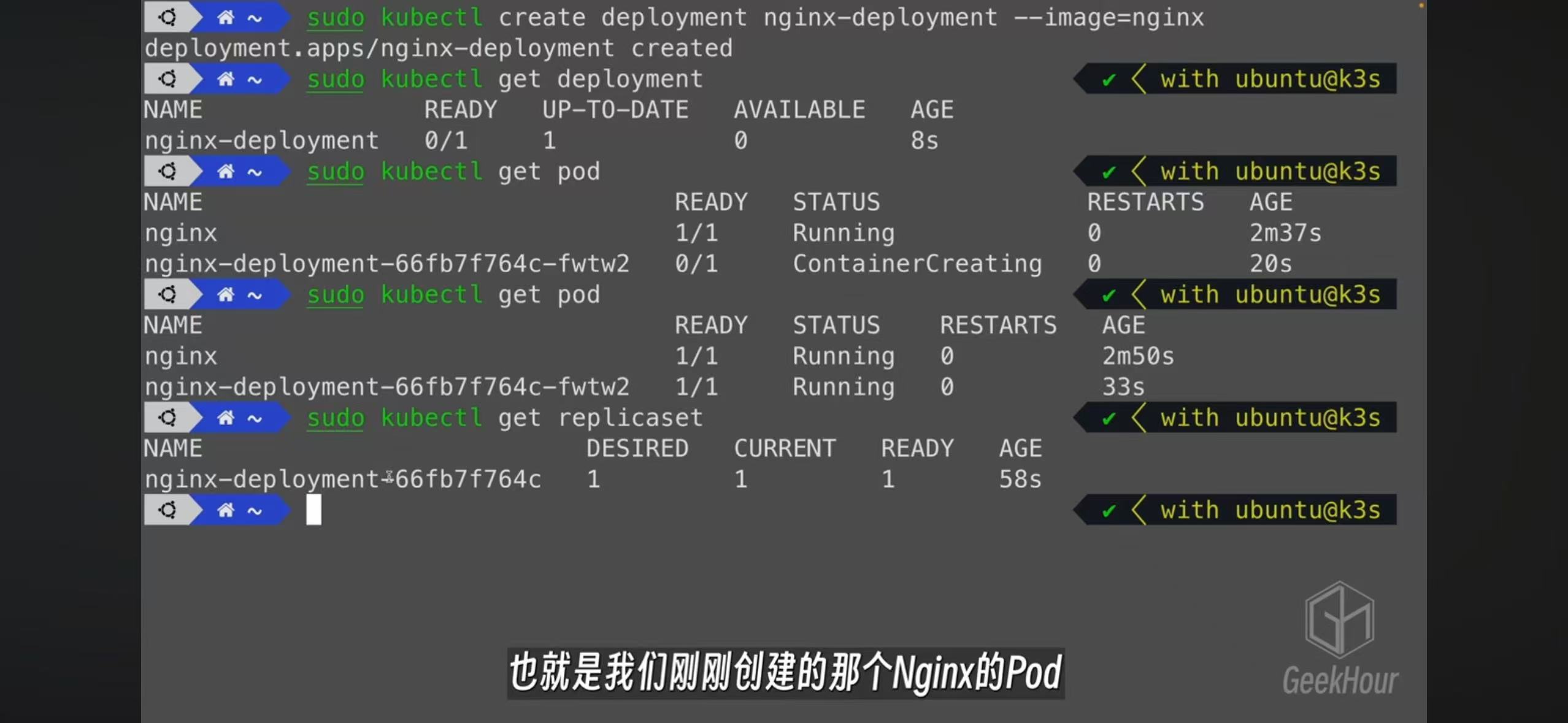
- Edit a deployment will automatically create cooresponding replicatset and pods
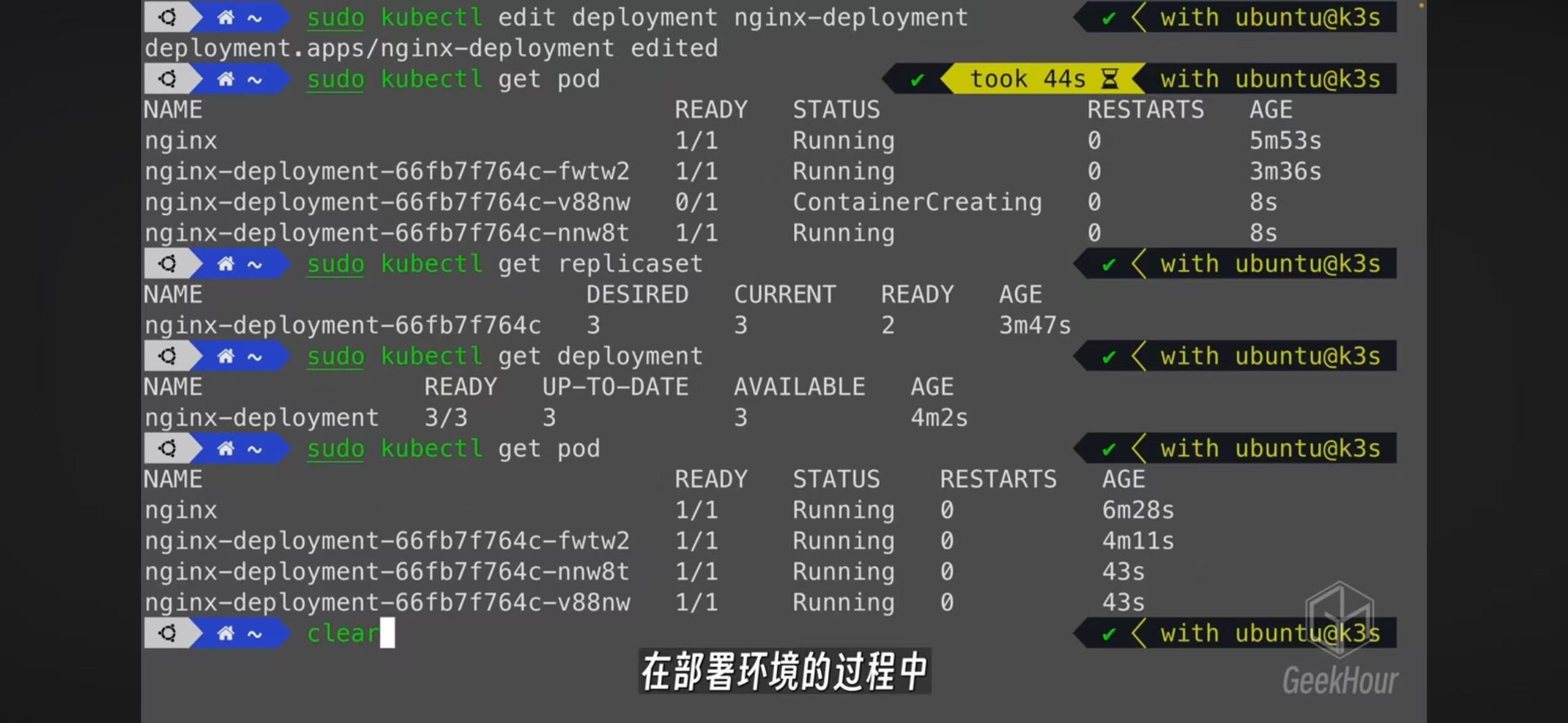
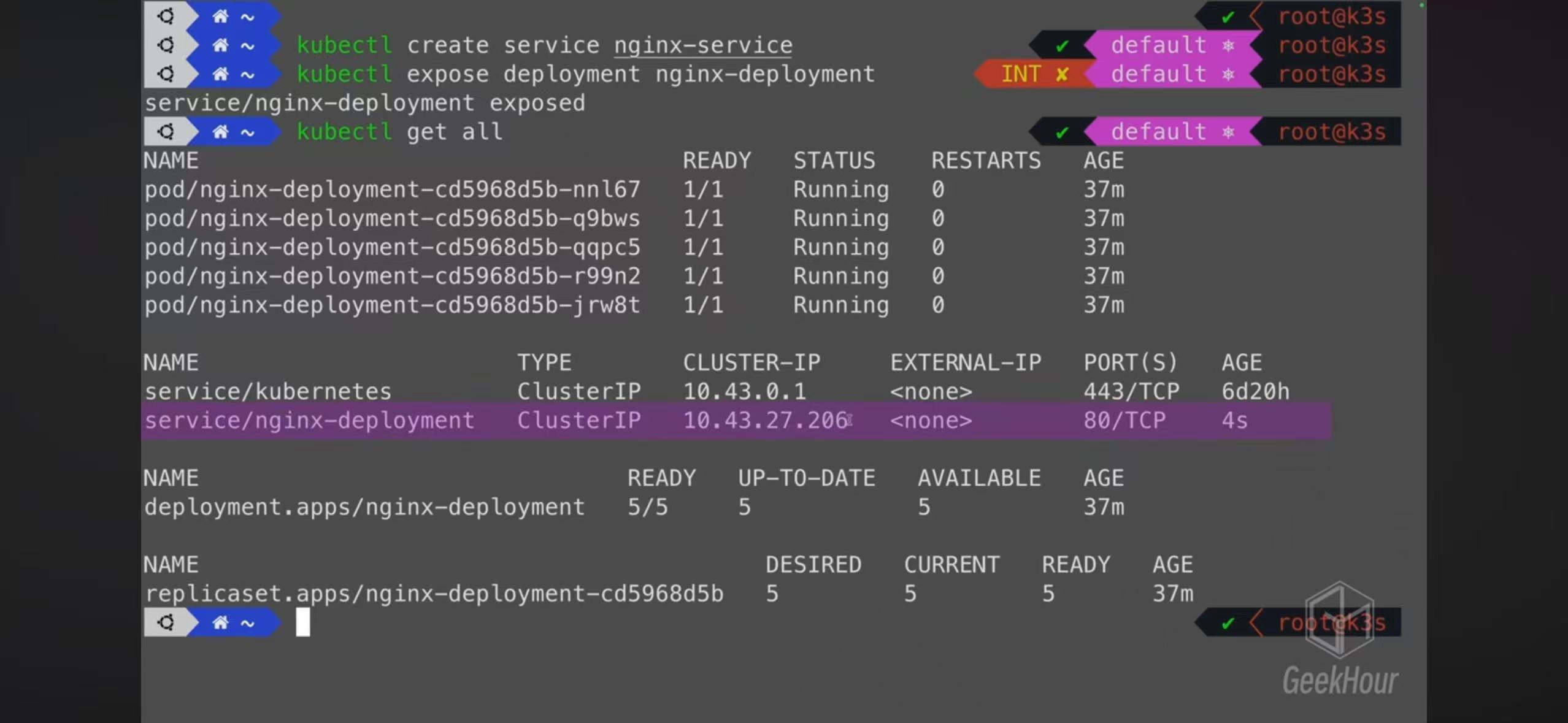
- You can create a service or expose a deployment
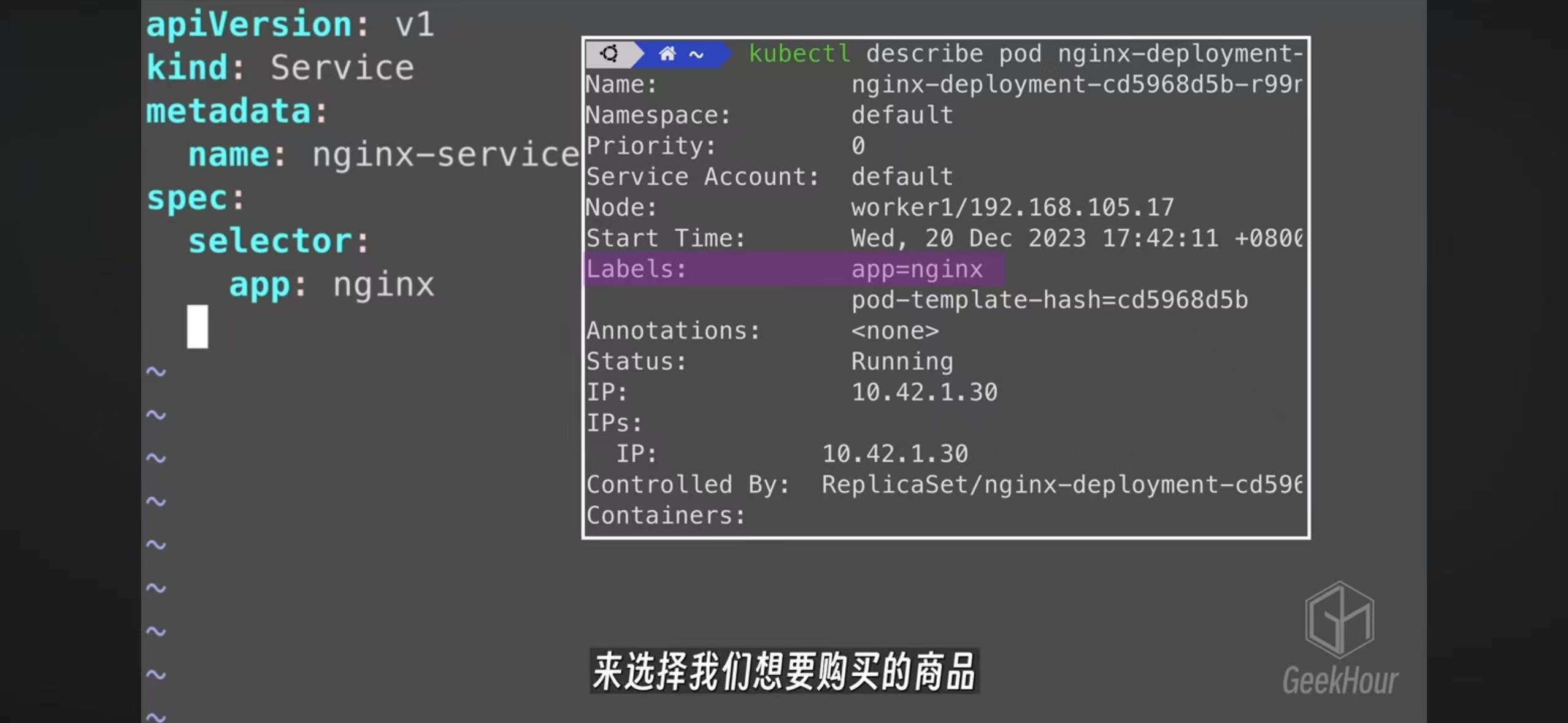
- The service config file use selector to match with pod labels
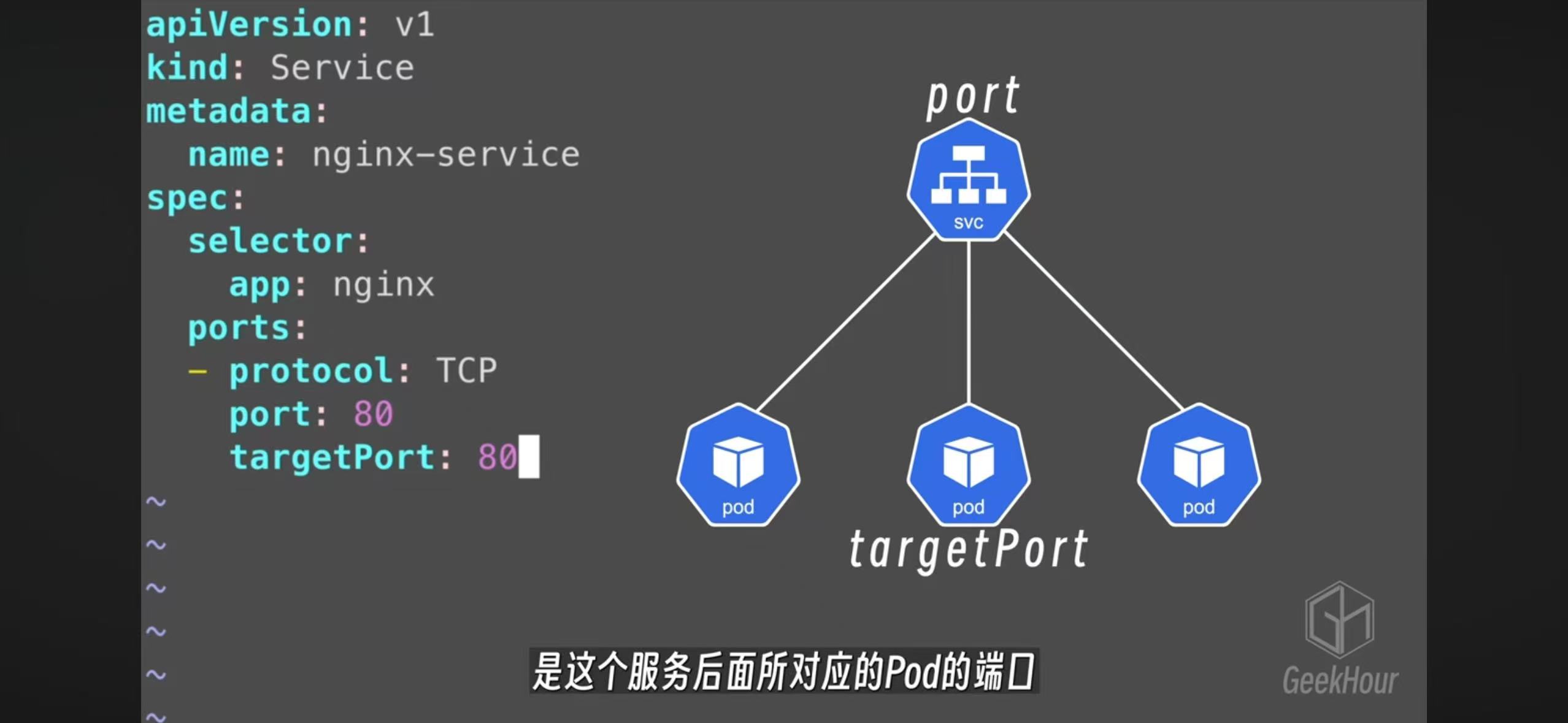
- The nodeport can map internal targetPort into external facing pord
Here are list of other service type
