Kubenetes 101
I finially started the learning of K8S, and followed this offical doc to get my pods listed, deployment done, and service created.
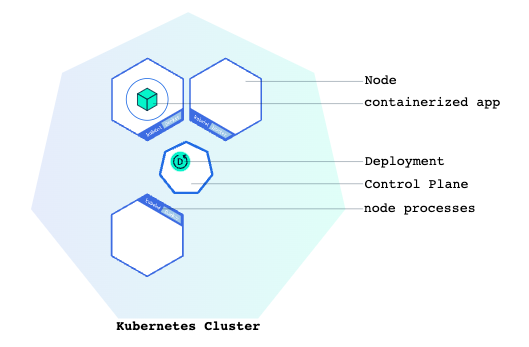
0 Cluster
The nodes and control panel concepts are familiar, and k8s can deploy containerized apps into nodes, single or multiple. That’s how it scales out applications.
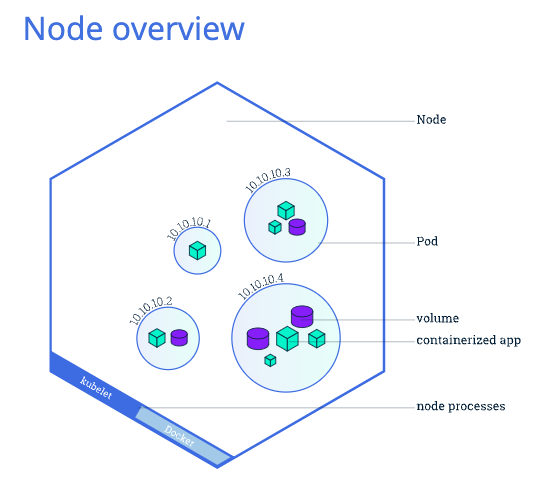
1 Pods
There are kubelet and docker runtime on each nodes, which is understanding.
The Pods are the basic unit of K8S applications and it scales out by pod
2 Basic operations
#alias kc=kubectl
# both singular and plural works
kc get pod/deploy/service
kc describe pods/deployments/services
kc logs "$POD_NAME"
kc exec -it $POD_NAME -- bash
3 Proxy and Service
All pods are internal traffic and not exposed by default. You can either use proxy and services to expose the pods
Assume the app is working on port 8080
# Running proxy
# you will see "Starting to serve on 127.0.0.1:8001"
kc proxy
# curl
curl http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/$POD_NAME:8080/proxy/
A Service in Kubernetes is an abstraction which defines a logical set of Pods and a policy by which to access them.
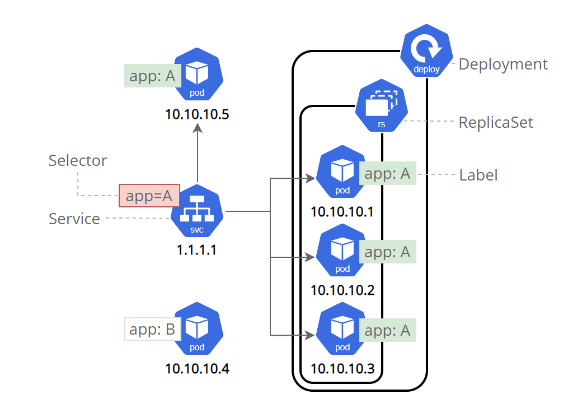
#To create a service
kc expose deployment/kubernetes-bootcamp --type="NodePort" --port 8080
# Get the port from kc get services/$sevice_name
# 8080:31617/TCP
curl http://localhost:31617"
4 Labels
Use label to easy identify pods
kc label pods "$POD_NAME" version=v1
kc get pods -l version=v1
5 Scale
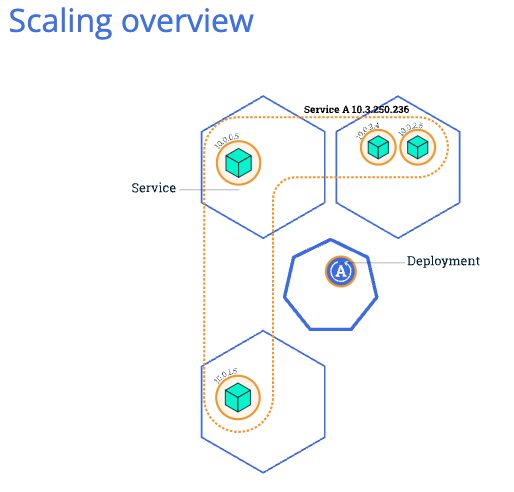
# Create service with LoadBalancer type
kc expose deployment/kubernetes-bootcamp --type="LoadBalancer" --port 8080
kc scale deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp --replicas=4
# list pods and IP
kc get pod -o wide
6 Update app
Update the application by setting new images to the deployment
kc set image deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp kubernetes-bootcamp=docker.io/jocatalin/kubernetes-bootcamp:v2
kc rollout status deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp
kc rollout undo deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp